Every parent undoubtedly has thisconcern any deviations in the child's health. One of the reasons for concern for parents is various rashes on the skin. Often, a rash appears after a high temperature or together with it. Any rash that worries you should be shown to a pediatrician. In some cases, you can take your time and calmly go to the doctor within a few days (if the rash does not go away on its own). In other cases, it is mortally dangerous and the count is not in days, but in hours. In this matter, it is necessary to understand and remember what to pay attention to.
Banal Sweating
The safest rash to occur afterheavy sweating of the body at elevated temperature is prickly heat. Prickly heat is a skin irritation that develops after heavy sweating and insufficient evaporation of sweat. It is often observed in infants and young children. Its development is facilitated by overheating and excessive wrapping of the child. Prickly heat appears as a skin rash in the form of small blisters with transparent-watery contents on closed areas of the skin (arms, legs, back, neck, buttocks). It can cause itching and anxiety in the child. Treatment consists of taking air baths and water procedures with a light solution of potassium permanganate, decoctions of oak bark or succession. Taking antihistamines in this case is inappropriate. To prevent urticaria, as well as to alleviate the patient's condition when the body temperature rises, adults should provide cool, moist air in the room and not wrap the child up. If this is not done, the likelihood of prickly heat will be several times higher.
Allergic reaction
At high temperatures, most parentsThey start giving antipyretic drugs, and in some cases, other medications. Each of the components of these drugs can be an allergen for your child and cause a rash. Contact allergy cannot be ruled out either (you put something new on your child or made the bed with clean linen). An allergic rash appears quite quickly after contact with an allergen and is a variety of itchy rashes on the skin. Often, an allergy is accompanied by a severe runny nose. When a rash appears, parents must analyze what new things they have given their child recently (medicines, food products, clothes) and, based on this, draw a conclusion - can the rash that has appeared be an allergic reaction. Treatment consists of eliminating the allergen from the child's environment (change the medicine, clothes, bed linen), taking sorbents (to more quickly remove the allergen from the body) and taking antihistamines prescribed by a doctor. If you suspect an allergy, you should consult a doctor, because if even the most minor allergy reoccurs, serious complications may arise, in particular - Quincke's edema. Mosquito bites also cause a skin allergic reaction, and a large number of bites can sometimes be mistaken for a rash.
Viral diseases
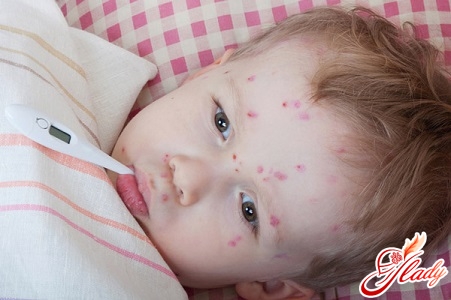
Herpes 6 and 7 types This virus is most oftencauses an infectious disease in young children (usually under two years of age), which is called sudden exanthema (roseola). Sometimes it is called pseudo-rubella. The disease begins with a high temperature. There are no other symptoms. On the 3-4th day from the onset of the disease, the temperature drops, and 9-20 hours after the temperature, a pinpoint pink rash appears. The rash is located all over the body. After this, the temperature does not rise again. Very often, the rash is mistaken for an allergic reaction of the body to antipyretics, which the parents managed to give the child during the days when the temperature was high. However, the rash goes away on its own in a couple of days without taking any medications. With roseola, no special treatment is required, the disease is not dangerous and does not cause any complications. Measles At the beginning of the disease, the temperature rises, there is a cough and a runny nose. The rash in a child appears on the 3-4th day from the onset of the disease. Small red spots (which can merge, turning into large spots) appear on the head and face and, gradually moving down, reach the feet in a couple of days. The disease is serious and quite difficult to bear. In our country, thanks to vaccination, it is rare. Rubella With rubella, fever and rash appear simultaneously, accompanied by symptoms of acute respiratory infections and enlarged lymph nodes on the neck and back of the head. The rash is small, pale pink. It spreads, like with measles, from head to toe, but more quickly - in a couple of hours, and disappears in 3-4 days. A child is considered contagious one day before the rash appears and 5 days after. Particular attention should be paid to isolating pregnant women from a patient with rubella due to the extremely unfavorable effect of the virus on the fetus (regardless of whether the woman gets sick after contact with the patient or not). Chickenpox The rash appears against the background of an increase in temperature and a deterioration in general health. The rash appears as red spots all over the body. After a couple of hours, these spots turn into blisters filled with a colorless liquid and begin to itch. On the second day, the liquid in the blister becomes cloudy, and the pimple itself wrinkles, dries up and becomes covered with a crust, which falls off after a week. New pimples will appear on the child's body within 3-7 days. The child is considered contagious the day before the onset of the disease, during the entire illness and 5 days after the appearance of the last fragment of the rash. This disease is most easily tolerated by children under 12 years old, older children tolerate it more severely, and for adults it poses a serious threat and often leads to complications.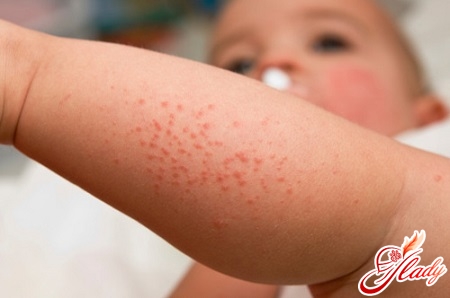
Bacterial infections
Scarlet fever An infectious disease, witha pronounced reaction of the body to erythrotoxin - a poisonous substance produced by some streptococcus bacteria. The onset of the disease is characterized by a sharp jump in temperature to 39-40 ° C. At the same time, the child may have a headache, nausea and, when swallowing, a severe sore throat. If you look into the child's mouth in the first hours after the onset of the disease, you will see that the tongue is coated with a white coating. Later, the tongue will become shiny and bright red, and a white coating appears on the tonsils. By the end of the first day, a small pink rash appears. It covers the entire body and thickens in the skin folds. To the touch, the skin is dry and rough, like sandpaper, and reddish in appearance, with a large number of brighter red dots. Another characteristic sign of scarlet fever is that the area around the mouth (nasolabial triangle) remains clear of rash and pale. A week after the rash disappears, the skin begins to peel very strongly (especially on the palms) - this is the death of epidermal cells, the outer layer of the skin, that died during the disease. With timely treatment of scarlet fever with antibiotics, the outcome of the disease is favorable, and if they are refused - severe complications are almost always. Quarantine of a child with scarlet fever (3 weeks from the onset of the disease) is not to prevent the child from infecting anyone, but to prevent further exposure to streptococcus bacteria during the time while the immune system is not yet strong, since this can lead to complications and allergic reactions. Meningococcal infection The most serious and deadly disease, in which the time before treatment is prescribed is not in days, but in hours - meningococcal meningitis. When the infection enters the blood through the bloodstream, it penetrates the brain. There is a form of meningococcal meningitis when meningitis involves blood poisoning. Symptoms of this form of meningitis are:
- high body temperature,
- rash in the form of hemorrhages under the skin in the form of asterisks (there may be only a few elements), which, if you press it with your finger, does not disappear,
- vomiting.
In case of high body temperature, vomiting and rash inin the form of subcutaneous hemorrhages (shaped like stars) that do not disappear when pressed with a finger, the child must be taken to a medical facility immediately. With timely treatment and the use of antibiotics, the disease is curable and does not cause complications. Vaccination is done to prevent meningococcal infections.
Your actions upon detection
If you notice a rash on your child, your firstthe task is to analyze the past few days to determine whether the rash is allergic. If it is an allergy, then eliminate the allergen. If you suspect your child has meningococcal infection, call an ambulance immediately. If you suspect an infectious disease, call a doctor at home (to exclude infection of others in transport and at the clinic) and isolate the child from pregnant women (until you are sure that this disease is not rubella). Before the doctor arrives, do not apply any medications to the rash, especially with dyes. Still, the diagnosis of the disease and the prescription of treatment should be made by a doctor. Only he can determine whether the child has a viral or bacterial disease, and if bacterial, prescribe a suitable antibiotic. Vaccination is carried out to prevent some of the diseases described above. Vaccinate according to the vaccination schedule, strengthen the child's immunity, try to avoid allergens and be healthy!









