
Subcutaneous lipomas (lipomas, fatty tumors)— benign subcutaneous nodes formed from fatty tissue on the human body. These tumors are painless and are not associated with surrounding tissues. Lipomas do not cause any discomfort to a person until they reach a diameter of more than 1 cm. Lipomas grow slowly, eventually reaching impressive sizes. That is when they begin to cause both physical and aesthetic inconvenience to their carrier, because a lipoma can even appear on the face. It also happens that lipomas form in places inaccessible to palpation (in the retroperitoneal tissue, in the lungs, in the mammary gland, etc.) Sometimes patients are bothered by multiple formations. Most often, lipomas are from 1 to 5 cm in diameter. But sometimes there are quite large sizes — more than 10 cm. In such patients, lipomas sag and form a stalk of skin at the base, which leads to blood stagnation, necrosis and ulceration. The size of the lipoma on the body can also depend on the patient's weight. For example, if the patient's weight increases, the size of the tumor also increases. But still, more often than not, the growth of the lipoma is uncontrolled. The appearance and development of lipomas is asymptomatic, but it also happens that they cause pain to patients, cause discomfort, and compress nearby organs. Although most complaints are about a cosmetic defect. You can get rid of lipomas surgically, but before the operation, you need to make sure that the formation is benign using a puncture biopsy.
Diagnosis of subcutaneous adipocytes
Lipomas are most often diagnosed on the bodywomen aged 30 to 50 years. Lipomas usually form under the skin in places where there is fatty tissue. The favorite places for lipomas are the back, arms, legs, head, both the hairy part and the face. Lipomas are classified according to the cellular composition into the following types:
- lipofibroma - a soft lipoma consisting mainly of adipose tissue;
- fibrolipoma - a dense lipoma consisting mainly of connective fibrous tissue;
- angiolipoma - a lipoma containing a large number of blood vessels;
- myolipoma - a neoplasm that contains smooth muscle fibers;
- myelolipoma is the rarest type of lipoma, consisting of fatty and hematopoietic tissue.
Causes of Lipoma
Today, the reasons for the appearance of lipomashave not been fully clarified. But scientists have some assumptions. It is believed that the occurrence of lipomas is associated with a systemic disruption of metabolic processes in adipose tissue. It is also not worth excluding the possibility of lipomas appearing due to hormonal disruptions in the body. These include: menopause in women, during which the reproductive function is restructured, and damage to the part of the brain responsible for metabolic processes in the body. The development of lipomas can be provoked by diseases of the liver and pancreas, problems in the functioning of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland. Often lipomas develop due to diabetes, malignant tumors of the respiratory tract, and also against the background of alcoholism.
Conducting examinations with lipoma
To get rid of lipomas on the body,First of all, it is necessary to conduct diagnostics. Diagnostics of lipomas located on the surface of the body is not difficult. The following factors are taken into account:
- location by lip;
- consistency;
- communication with surrounding tissues;
- painlessness when feeling;
- the formation of retraction when stretching the skin over the wen.
If it is necessary to remove a lipoma located ininaccessible for palpation and inspection places, then X-ray and ultrasound examination are prescribed. X-ray examination of soft tissue lipomas is based on the use of long-wave X-ray radiation, which allows to evaluate the structure of the tissues of the formation. The most reliable method for diagnosing deep-lying lipomas is computed tomography, which can distinguish fatty tissue from denser ones. If during the examination there are doubts about the benign nature of the tumor, then they resort to the methods of puncture biopsy and cytological examination. Before surgical intervention to remove the lipoma, a laboratory study is carried out, which includes:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- blood glucose;
- research on HIV, hepatitis, syphilis.
In some cases, before getting rid of a lipoma, it is necessary to exclude other diseases. For this, a cytological study is performed.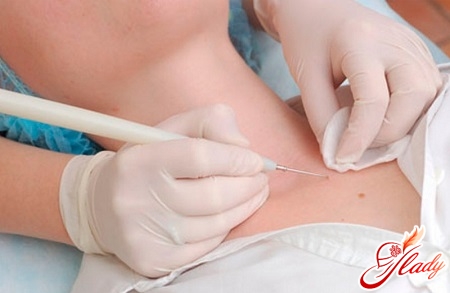
Treatment of subcutaneous adipocytes
The only way to get rid of lipomas is by surgical means. There are the following indications for this:
- a rapid increase in the size of the wen;
- large tumor size;
- painful sensations due to squeezing the surrounding tissues of the lipoma;
- aesthetic defect.
If the subcutaneous lipoma is small and located inaccessible place, it can be removed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. If the lipoma is large or located on the body in complex anatomical places (neck, armpit), then patients are hospitalized and treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. There are 3 methods of surgical intervention to remove lipomas:
- removal together with the capsule - the mostradical method of treatment. Under local anesthesia, a wide skin incision is made, the lipoma is enucleated and removed along with the capsule. After this, stitches are applied to the skin and subcutaneous fat. This method is the most effective, eliminates the manifestation of relapses, but from an aesthetic point of view it is unsatisfactory.
- Minimally invasive removal of lipoma - method,in which a cut less than 1 cm long is made on the skin. The lipoma is destroyed and removed inside the capsule. The advantage of this method is a good cosmetic effect, but the method is not radical.
- liposuction of lipoma - a method in whichAn incision no longer than 5 mm is made in the skin. The lipoma is removed inside the capsule using a lipoaspirator. This method of surgical intervention achieves a good cosmetic effect, but there is a risk of relapse.

Complications of lipoma
Complications with lipomas are extremely rare. Here are the main ones:
- inflammation - the lipoma turns red, increases in size and begins to hurt. When pressing, the tumor feels like it contains fluid;
- liposarcoma - a malignant lipoma, into which, in very rare cases, an ordinary lipoma can degenerate;
- displacement of surrounding tissues near the lipoma.
Getting rid of a lipoma is only half the battle,in the postoperative period, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the area of the body where the operation was performed to exclude complications. Lipoma is a benign neoplasm that may not bother its carrier for a very long period of time, remain unchanged in size or grow very slowly. Of course, the appearance of a lipoma is not attractive, so every patient dreams of getting rid of the tumor as soon as possible. Moreover, injuries or damage to the lipoma can cause it to change up to degeneration into a malignant tumor. Usually, the prognosis for treating lipomas on the body is favorable, and getting rid of them is not at all difficult, especially for an experienced and qualified doctor. The most important thing is not to delay treatment and undergo an examination as soon as possible so that the doctor can choose the most appropriate removal method.









