Melanoma is malignant and veryan aggressive skin tumor that develops as a result of the degeneration of melanocytes and melanoblasts - pigment cells that produce the pigment melanin. The tumor contains a large amount of melanin in its cells - this is what causes the dark color. But sometimes there are also variants without pigment. Of all skin tumors, only 10% are melanoma. Recently, a continuous increase in the incidence of this disease has been noted. The number of diagnoses of skin melanoma has increased significantly over the past decades. It is noted that at the age of sixty, both women and men get sick with the same frequency. The peak incidence rate falls on the age range from thirty to fifty years. For those who already have melanoma, the risk of developing a new one is about twelve percent. The prognosis for this disease is extremely unfavorable - In the structure of mortality, skin melanoma is in ninth place (1% of patients with malignant tumors die from melanoma).
The causes of melanoma
The main reason for the occurrence of melanoma is— the effect of ultraviolet radiation on open, unprotected areas of the skin. Ultraviolet radiation is carcinogenic, especially in squamous cell and basal cell skin cancer. Intensity will mean a lot for the development of skin melanoma. Most often, melanoma occurs as a result of a single exposure to high-intensity ultraviolet radiation. It can develop in patients who received sunburn in childhood or adolescence, and it often occurs in people who spend most of their time indoors and go on vacation to hot countries. Injuries to existing pigmented nevi can play a significant role in the development of melanoma. But it cannot be ruled out that due to injury, the tumor does not begin to grow, but only accelerates its development, since it arose long before that. These can be single effects on nevi - a bruise, a cut, abrasion — or chronic exposure: rubbing with chains, hard parts, seams of clothing, etc. Many scientific studies are devoted to the study of heredity in the etiology of the tumor. For example, it has been established that in those families where dysplastic nevus syndrome is present, there is an increased risk of developing skin melanoma. Those who have this syndrome can develop many dysplastic nevi throughout their lives - their number can be more than 50 with a very high risk of degeneration into melanoma. This syndrome has an autosomal dominant inheritance type. Therefore, when diagnosing, all close relatives should be sent for examination to an oncologist. It is highly desirable that such patients contact an oncologist for a follow-up examination every six months in order to promptly detect signs of the disease. More and more often, much attention in the development of such a disease as skin melanoma has been paid to immune factors. Immunodepression, like immunodeficiency states, - these are factors that contribute to the development of this disease. The influence of hormonal status on the development of skin melanoma has also been established, especially in women. Puberty, climacteric changes, and pregnancy can have a stimulating effect on the malignancy of existing pigment nevi.
Classification of melanoma, stage
There are four stages in the development of melanoma:
- the first stage: melanoma up to 2 mm thick, regional and distant metastases are absent.
- stage two - melanoma thicker than 2 mm, no regional or distant metastases.
- the third stage is set when damage to the regional lymph nodes is noted.
- The fourth stage is set if distant metastases are detected.
Melanoma most often metastasizes to the liver andlungs. Possible damage to the skin, skeletal bones, brain. With visceral metastases, the prognosis can be extremely unfavorable, life expectancy can be on average six months. According to prevalence and histological variant, melanoma can be divided into three main forms:
In addition, you should know that in addition tomelanoma can occur on the skin surface in the vascular membranes of the eyes, under the nail plates, on the mucous membranes (nasal cavity, conjunctiva, rectal mucosa, vagina), on the scalp. Such localizations, however, are very rare.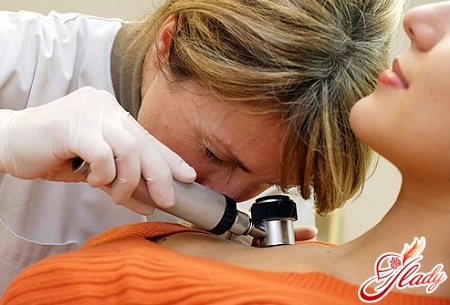
Diagnosis of the disease
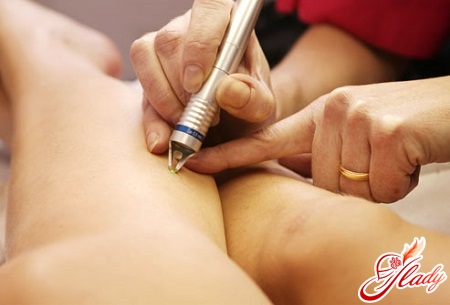
Despite the availability of melanoma for examination,Difficulties may arise in making a correct diagnosis. Sometimes it is impossible to distinguish melanoma from a pigmented nevus, and careful attention to the conversation with the patient can be of great importance for making a correct diagnosis. If melanoma is suspected, a morphological examination should be carried out. The final diagnosis can be established with its help. Cytological examination is performed in the presence of ulceration - smears are taken from the surface of the tumor. If there are doubts about the diagnosis, the main method for establishing the correct picture is an excisional biopsy (it involves complete excision of the tumor with a deviation from its edges of 2-5 mm), immediately after which a histological conclusion should be made. If the diagnosis is confirmed, wide excision should be performed immediately. The biopsy should be performed under general anesthesia, when piercing the melanoma area with a needle, it is possible that the tumor cells will spread to the surrounding tissues. To assess the spread of the tumor process, if melanoma has already been diagnosed, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the regional lymph nodes, an X-ray of the chest organs, and an ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Symptoms of melanoma
A competent doctor is able to understand wellpathological elements and neoplasms on the skin surface, but to the average person, pigment changes will mostly seem like a regular mole. In order not to miss the appearance of melanoma, it is necessary to know some symptoms, characteristic features of this disease. The first symptoms and signs of skin melanoma include:
- change in tumor size - slow growth.
- the tumor can acquire a convex shape.
- The color changes, unevenly colored areas appear.
- the outlines change, appear rugged, irregular edges.
- asymmetry.
- bleeding, the appearance of crusts.
- itching, the sensitivity changes in the tumor area.
The most common complaints from patients arethe appearance of a pigmented formation or an increase in the size of an existing one, itching and burning in the tumor area, bleeding occurs. Melanoma symptoms can be both primary and secondary. Additional signs include the absence of a skin pattern, hair loss in this area, peeling skin, and the appearance of seals on the surface of the tumor. The lymph nodes closest to the tumor may enlarge.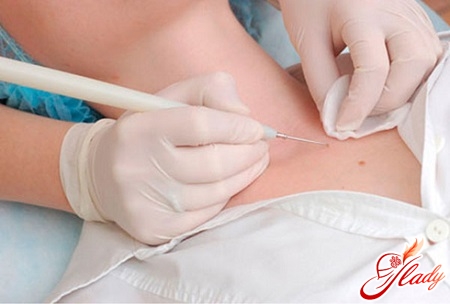
Prevention of melanoma
To prevent the occurrence of melanoma, you shouldLimit sun exposure. If a person is at risk, they should use sunscreens with a protection factor of at least 15, wear light, closed clothing, and be sure to wear a hat. Some types of melanoma have a hereditary predisposition, so if any relatives have ever been diagnosed with melanoma, they should be examined regularly by a dermatologist.
How to treat melanoma
Melanoma of the skin is mainly treated withsurgical methods. This provision is applicable both to the primary lesion and to metastases to the regional lymph nodes. Other types of treatment, which include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, cannot be considered an alternative to surgical intervention. But these methods can be used in the case of a widespread tumor process, with the appearance of distant metastases. Treatment of melanoma - 1-2 stages Treatment of skin melanoma by surgical methods should be performed under general anesthesia in a specialized oncology department. Early recognition of melanoma and its timely excision are the basis for successful treatment, the result of which can be complete elimination of the dangerous disease. Radical intervention is understood as excision of the tumor with the capture of the surrounding skin, subcutaneous fat under it, fascia or aponeurosis. The smallest indentation from the edge of the tumor can be 1 cm. After excision of the melanoma, it is not always possible to eliminate the defect by simply bringing the edges of the wound together. Different types of plastic replacement can be performed - for example, plastic surgery using a free skin flap, local tissues, transplantation of flaps with an axial type of blood supply is possible. Treatment of melanoma: stage three After excision of the melanoma, the disease often continues to progress. Most often, this is manifested by metastases of regional lymph nodes, which patients can detect themselves or this becomes clear during ultrasound. Lymphatic collectors are mainly located in the axillary and inguinal areas. To confirm the diagnosis, a fine-needle biopsy is performed on an enlarged lymph node. If melanoma cells are detected, the entire lymphatic apparatus in this area is removed as a single block with the surrounding tissue. The operation is traumatic, in the postoperative period it is often accompanied by lymphorrhea, that is, the outflow of lymph. A drain should be installed in the wound cavity - a hollow rubber tube that will facilitate the outflow of lymph from the wound cavity. In the postoperative period, additional treatment methods can be carried out - chemotherapy, radiation therapy. Treatment of stage four melanoma Despite the unfavorable prognosis, for this category of patients, it is possible to carry out treatment in order to prolong life, for which a variety of modern methods are used. As indications for surgical intervention, the following can be distinguished:
- removal of a single metastasis, if there are no other lesions, and the patient's general condition is good;
- elimination of symptoms that significantly reduce the quality of life of the patient or threaten life.
- decrease in tumor mass to increase sensitivity to chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy for melanoma
Treating Melanoma with Chemotherapyare used in patients with distant metastases. It is possible to achieve stabilization of the process using modern chemotherapy regimens only in twenty percent of cases, i.e. the efficiency is quite low due to the low sensitivity of melanoma to drugs. In case of a widespread tumor process, radiation therapy can be used. It is used mainly in the presence of distant metastases in the brain or localized bone lesions. The efficiency of this method is much inferior to surgical, therefore the indications for this method of treatment are limited.