Meningitis in children.This disease has been terrifying more than one generation of parents. Remember how our parents always scared us as children – “put on a hat immediately, otherwise you’ll catch a cold and get meningitis”? Surely, this phrase is familiar to everyone. However, a child, as a rule, does not go into detail about what kind of disease meningitis is, and therefore treats it with great disdain. And only after becoming adults and having their own children, parents begin to be more consciously afraid of this disease. Parents have a huge number of questions, one way or another related to this disease. This article is intended to help parents understand whether the devil is as bad as he is painted – in this case, meningitis in children.
Meningitis in children.This disease has been terrifying more than one generation of parents. Remember how our parents always scared us as children – “put on a hat immediately, otherwise you’ll catch a cold and get meningitis”? Surely, this phrase is familiar to everyone. However, a child, as a rule, does not go into detail about what kind of disease meningitis is, and therefore treats it with great disdain. And only after becoming adults and having their own children, parents begin to be more consciously afraid of this disease. Parents have a huge number of questions, one way or another related to this disease. This article is intended to help parents understand whether the devil is as bad as he is painted – in this case, meningitis in children.
Causes of the disease
So what is meningitis?Doctors call this an inflammatory process that involves the membranes of both the spinal cord and the brain. Please note that it is the membranes of the brain that become inflamed, not the cells themselves. In other words, the inflammatory process in meningitis develops outside the brain or spinal cord. Of course, any inflammatory process must be provoked by one or another factor. And meningitis is no exception - its development can be provoked by a variety of pathogenic microorganisms, such as fungi, viruses and bacteria. Moreover, a lot depends on the state of the child's body at the time of penetration of pathogenic bacteria. And the general condition of the child is also extremely important. For example, there is a misconception that meningitis is a purely childhood disease. However, this is not true at all - a person can get meningitis at absolutely any age. Why is this opinion formed? This is explained very, very simply - the worse the body's immune system works, the higher the risk of developing meningitis. And children by definition have an immature immune system – such are the physiological characteristics of a child’s body. And, therefore, children are more susceptible to this disease – this explains the misconception that meningitis is an exclusively childhood disease. But there are also certain risk groups among children, whose chances of getting meningitis are much higher than everyone else. These risk groups include:
Of course, there are many other reasons,which can provoke the development of meningitis in children. However, it is quite difficult to tell about everything, we have to limit ourselves to only the most common causes, which have already been mentioned above. Very often, frightened parents who have encountered this disease ask the doctor about the consequences that meningitis in children can entail. The answer to this question is ambiguous. Most often, meningitis passes almost without a trace, leaving no consequences or complications. As a rule, this is exactly what happens, provided that the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner, and the treatment is competent and appropriate. However, quite rarely, but still there are exceptions to this rule. Complications can occur, and sometimes quite serious, such as partial or complete loss of vision, hearing loss or even deafness, severe developmental delays in the child - both physical and mental. In especially severe cases, the child may fall into a coma or even die. As a rule, such terrible complications develop if parents do not seek medical help, or seek it too late. Fortunately, these complications are becoming less and less common. According to medical statistics, complications of meningitis currently occur in no more than 2% of all cases of the disease. And repeated meningitis in children is extremely, extremely rare - as a rule, only if the treatment was inappropriate, and it was not possible to completely cure the disease. This happens especially often if the parents were self-medicating. Self-administration of antibacterial and other drugs, if you are very lucky, can only eliminate the external manifestations of the disease for a short time. Therefore, in order to avoid such terrible consequences, at the first signs of the disease, you must seek medical help from doctors as soon as possible.
Signs of meningitis
Meningitis in children occurs in a very severe form.An experienced doctor does not have to make much effort to diagnose the disease - its symptoms are too specific and easily recognizable. Parents of small children should also know the main symptoms of the disease so as not to miss its onset. Meningitis in children, symptoms:
- Increased body temperature.The child's body temperature rises very sharply and to very high numbers - up to 40 degrees and higher. The child is extremely lethargic or, on the contrary, excited, can either sleep for a long time straight, or cry uncontrollably for a very long time - it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the central nervous system of the child. In addition, often in such a state the child can experience a strong feeling of chills. Older children can complain to their parents that they are cold, while younger ones simply shiver. It is almost impossible to bring down such a temperature by giving an antipyretic drug, as with a common acute respiratory disease.
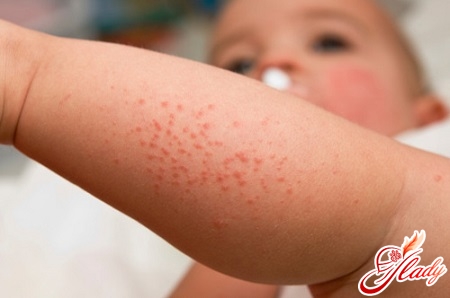
- Appearance of a rash. As a rule, on the first, and less often on the second day of the disease, all children without exception develop a pronounced hemorrhagic rash.
- Meningeal symptoms.Around the same time, the first meningeal symptoms appear, which doctors discover during the examination of the child. First of all, the doctor will perform a puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid. As a rule, during its subsequent examination, it is discovered that it is either milky or dirty yellow in color, cloudy. The content of leukocytes and neutrophils in it is significantly increased, and bean-shaped diplococci can be found in the cytoplasm, and the protein content is increased. The glucose content is very much reduced. If you do a culture, you can easily determine the type of pathogen that caused the development of meningitis.
When examining the blood test of a sick childextremely pronounced changes are detected, indicating a severe inflammatory process occurring in the body. All these signs clearly indicate that the child is sick with meningitis and needs immediate treatment.
Varieties of meningitis
There are several types of meningitis inchildren. These varieties depend on what pathogen caused the development of meningitis in the child. Doctors distinguish several main varieties of this disease:
- Pneumococcal meningitis
In case meningitis is caused bypneumococci, doctors talk about pneumococcal meningitis. Very often this disease is preceded by either pneumonia, or sinusitis, or acute otitis. However, this is not a mandatory condition - in about half of all sick children, this type of meningitis is primary, without any previous diseases. The disease begins to manifest itself quite quickly and in an acute form, but the meningeal syndrome itself manifests itself a little later than in all other cases - approximately on the third day, not earlier. However, the progression of this type of meningitis is very, very active - the child's consciousness becomes clouded very quickly, and nerve paresis develops. When performing a spinal puncture, it can be found that the cerebrospinal fluid contains a huge percentage of pus, leukocytes and pneumococci. This form of the disease is one of the most dangerous of all existing ones. Doctors explain this feature by the fact that the ventricles of the brain and its substance itself are extremely quickly involved in the inflammatory process. This is why parents should seek medical help from a doctor as soon as possible, at the first symptoms of the disease.
- Hemophilic meningitis
This type of meningitis is caused by Haemophilus influenzae.bacillus. Most often, this disease affects children under one year of age, but it can also occur at an older age. The first manifestations of this disease can be very different - both acute meningeal and catarrhal, similar to those typical of acute respiratory diseases - runny nose, cough, sore throat. In the latter case, meningeal symptoms themselves appear on the fourth or even fifth day. Moreover, doctors warn parents of small children to be extremely attentive to the slightest discomfort of their baby. And if symptoms such as frequent regurgitation, vomiting, excessive swelling of the fontanel, cessation of its pulsation and causeless crying appear, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance team or take the child to a medical facility yourself.
- Viral meningitis
In the event that meningitis developsdue to certain viruses, the onset of the disease will also be slightly different. Strictly speaking, the disease occurs in two stages - first, the child develops a viral disease, and then - signs of meningitis itself appear. However, meningeal syndrome manifests itself a little differently than in other cases of the disease. Despite the fact that the sick child experiences severe headaches and a depressed general condition, the meningeal symptoms themselves are expressed quite weakly. Often they are far from always expressed in full, and disorders of consciousness, which are typical for all other forms of meningitis, practically do not occur in this situation. Changes in the blood test in this situation are more similar to those that occur in the blood of a child sick with viral diseases than to those that occur with meningitis. However, if the child does not receive proper and timely treatment, these changes may appear in a few days.
- Tuberculous meningitis
Tuberculous meningitis is the most rarea common type of this disease, but, unfortunately, they also occur. Until recently, the mortality rate for this type of meningitis was quite high, recently modern medicine has learned to cope with this problem and mortality has been almost eliminated. However, tuberculous meningitis is still a serious threat to the health and life of a child. It also manifests itself quite unusually, and its course is typically atypical. Therefore, there is a real threat that the disease will be diagnosed untimely, and, accordingly, treatment will also begin untimely, as a result of which a very large amount of time is lost. And it is extremely difficult to cope with this disease. As a rule, the disease begins with a fever, after which he begins to vomit and headaches.
Problems in the diagnosis of meningitis
In some cases, the diagnosis of meningitisis too complicated even for experienced doctors. This happens when doctors or parents themselves, having decided that the child has one or another inflammatory disease, begin a course of treatment with antibacterial drugs. As a result, the clinical picture of meningitis becomes blurred. For example, the fever is not so pronounced - the body temperature can remain at 37 - 38 degrees. The headache is also not as strong as usual, but is regular. Nausea and vomiting are almost always present, and quite debilitating.
Treatment of meningitis
There is no need to describe the treatment of meningitis in detail.there is no point – self-medication in this situation is absolutely unacceptable. Treatment should be carried out only under strict medical supervision, and exclusively in a hospital setting. This requirement is explained by the fact that meningitis is a very insidious disease – the child’s condition may become critical, and emergency resuscitation measures may be needed, which are only possible in a hospital setting. Doctors will conduct a full examination of your child and prescribe the necessary treatment, which will help suppress pathogenic bacteria fairly quickly. And very soon there will be no trace of the disease in your child, provided that you seek help from doctors in a timely manner. Often, parents ask their children’s local doctors whether the meningitis vaccination is effective for children. On the one hand, such a measure can be quite effective in certain cases – during periods of increased incidence of this disease, in unfavorable areas, for children who fall into a high-risk group. However, we must not forget that the vaccination can protect a child only from one or another type of meningitis, but not from all of its varieties. Therefore, there is always a risk that the child will still encounter meningitis. And the vaccination in any case protects the child for no more than 4 years. After that, the next vaccination is necessary. And there are no other methods of non-specific prevention of this disease. The only thing that parents can do is to be attentive to the health of their child. And at the first symptoms of meningitis, seek medical help as soon as possible. This will help save not only the health, but also the life of the child. We recommend reading: