Today, all over the world, includingand in our country, thousands of people die and fall ill every day. Very often the cause of death is acute blood loss. Almost any medical institution currently experiences a shortage of donor blood. In many cities, special centers for transfusion and blood collection from donors are being created, thereby replenishing the blood bank (reserves). Blood reserves should be available in any hospital. It is desirable that it be fresh and necessarily with an unexpired shelf life.
The relevance of this topic
Some people are regular donors.blood. Before studying the frequency of donating this important component, it is necessary to understand some concepts. So, a donor is a person who gives blood. It can be whole, in the form of plasma, red blood cells or white blood cells. An acceptor is a person who perceives the missing blood from a donor, needs it. Blood transfusions are very often carried out for leukemia and other blood diseases, severe injuries with blood loss, shock and other emergency conditions. Let's consider in more detail how often you can donate blood, health safety during this medical procedure. But before that, it is important to find out who can be a donor, because there are certain restrictions.
Who can become a blood donor?
In order for a person to be able to donate blood, he/shemust meet certain criteria. Firstly, he or she must be between 18 and 60 years old. This is very important, since this is the period when the circulatory system matures. Secondly, most blood donation centers will require local registration. This is necessary in order to know where to find this person if necessary. Thirdly, a passport or other identity document is required. Fourthly, there are time restrictions that do not allow you to donate blood at the moment. These include the presence of colds or not having passed 1 month from the day of recovery from acute respiratory infections. It is not allowed to donate blood within 10 - 30 days after vaccinations. After tooth extraction, 10 days will also have to pass. After the birth of a child, tattooing or piercing, you must wait 1 year. There are separate provisions for women. It is very important that the donor is not pregnant at the time of donation, at least 5 days must have passed since the day of the last menstruation. In addition to temporary reasons, there are also permanent reasons for refusal to donate. These include: blood diseases, previous homosexual relationships, past or present viral hepatitis, the presence of promiscuous sexual relations in the donor, myopia, mental disorders, high blood pressure, drug addiction, alcoholism, syphilis, HIV infection and some others.
Periodicity of blood donation
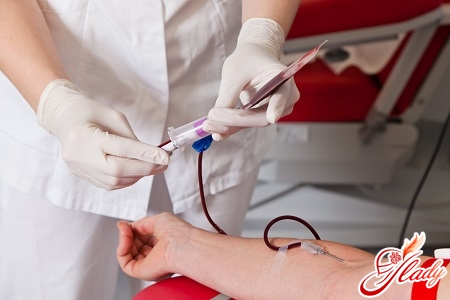
Many will ask the question:How often can you donate blood? The answer is quite simple. Whole blood is officially allowed to be donated no more than 5 times a year for males and no more than 4 times for women. It is very important that the intervals between these procedures are at least 60 days, that is, 2 months. All this is of great importance, since with more frequent blood donation, the blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes) do not have time to mature fully, which can lead to slight anemia and deterioration in health. Separately, it is necessary to highlight the donation of plasma. The fact is that today it is not whole blood that is donated more often, but its components. This makes the work easier. As for plasma, in total it is allowed to donate no more than 12 liters per year. Plasma is the liquid part of the blood without formed elements: erythrocytes, platelets and leukocytes. Donation of platelet mass is allowed no more than once a month, despite the fact that platelets in the blood are restored after a week. This may be due to the fact that very often the dose of platelets taken with the help of special equipment is somewhat higher than required. It is also very interesting how much blood can be donated at a time in volume terms in a particular institution. The full dose is 400 ml. If a person is doing this for the first time, it is only 200 ml. With some deviations in health, the dose can be reduced to 350 ml.
Preparing for blood donation
Before taking the necessary material froma person, he must undergo a quick examination. It includes a blood test, determination of the Rh factor and group, hemoglobin level. In addition, it will be necessary to measure blood pressure, weight. Then a documentary agreement is drawn up with the donor's signature. Of great importance is the fact that a person of a certain weight (at least 50 kg) can donate blood, it is important to take into account his appearance, the presence of exhaustion. Before the medical examination, it is recommended to carefully prepare for the procedure a few days in advance. In order for the blood to be suitable for the patient, the following rules must be followed. Do not drink alcoholic beverages 2 days before the procedure, do not smoke a few hours before donating blood or plasma, since various harmful substances can enter the blood. 3-5 days before, you must exclude from use certain medications: aspirin, painkillers, etc. Before the procedure itself, you need to have breakfast and drink a glass of liquid. Diet is also very important. The following foods should not be consumed the day before blood sampling: eggs, milk and dairy products, cheese, butter, nuts, bananas, salty, spicy, fried and smoked foods. It is optimal to consume fruits, except bananas, vegetables, bread, cereals, fish, juices, and sweets during this period.
Influence of donation on the human body
It should be noted that donation is very beneficial.In addition to the financial side (payment for blood), thanks to this procedure you can constantly and most importantly free of charge monitor your health. This is possible thanks to the tests that are taken before blood collection. The second positive aspect is the increase in immunity. With each collection of one or another component, the blood composition is updated, and this ensures better circulation and blood supply to all organs and tissues. In addition, this is an excellent way to adapt to unfavorable factors, such as blood loss, injuries. According to experts, male donors are 30% less likely to have heart attacks. Regular blood donation can increase a person's life expectancy. It improves metabolism, increases the efficiency of hematopoietic organs, and increases the mobilization of the body's forces. But, nevertheless, donation is to some extent unsafe. Fainting and weakness are possible with this procedure. However, all this is temporary. There is a risk of transmitting some infections, including HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, but this is possible only if the collection technique is violated. Paying for blood is another weighty argument. The cost of a portion of blood in Russia ranges from 300-400 rubles to one and a half thousand. In addition, the donor is entitled to 2 days off: 1 - on the day of collection, and the second at the person's choice.
Conclusion, conclusions, recommendations
It is possible to draw a conclusion about what to hand overblood or its individual components - it is not only profitable, but also useful for the body. The frequency of donating whole blood depends on gender: for men it is no more than 5 times a year, for women - 4. It is important that the interval between procedures is not less than 60 days. This time is necessary for the restoration and replenishment of the components of the bloodstream. You can donate whole blood or its components, for example, plasma. It is allowed to donate plasma in a volume of no more than 12 liters per year. As for platelets, despite their rapid restoration, it is advisable to donate them no more than once a month. The volume of a portion of blood can vary from 200 to 400 ml. Examination and preparation for this manipulation are of great importance for donating blood. It is strictly forbidden to carry out the procedure on a patient with a history of HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis and some other infectious diseases. If blood collection is performed correctly and the examination is thorough, the risk of complications is virtually non-existent for both the donor and the recipient.