
Mastopathy is becoming widespreadcommon female disease. Cystic fibrous mastopathy is a wide range of benign pathological changes in the tissues of female mammary glands. Small seals, swelling of the mammary glands, accompanied by pain syndrome, periodically occur in almost every woman. These completely physiological phenomena are often associated with the activation of hormonal processes in the mammary glands, and there is no need to treat them. Despite the unpleasant manifestations, most forms of mastopathy (formed cystic or fibrous) are not dangerous. But mastopathy, especially in the nodular form, can complicate the diagnosis of malignant tumors, and sometimes contribute to their development. It is possible to identify signs of cystic fibrous mastopathy from the very beginning, but often these symptoms remain unnoticed for a long time due to the similarity with periodic manifestations of mastalgia. It is not considered a deviation from the norm, but can progress, becoming constant, independent of the periodicity of the menstrual cycle, and persistent changes of the cystic or fibrous type may appear in the mammary glands. With mastopathy, swelling, a feeling of distension and pain in the mammary glands increase and from cyclical can become constant. The nature and intensity of pain can be different: dull, aching, stabbing, burning. They affect both or one mammary gland, localized in some one place or covering the entire organ. Soreness of the nipples, a change in their shape, and sometimes - the release of fluid from them may be observed. Particularly painful limited areas of seals are palpated in the tissues of the mammary glands, which do not dissolve after the end of the menstrual cycle. Changes in the relief of the skin and the shape of the mammary glands are possible. With nodular mastopathy, seals, compared to seals characteristic of the diffuse form, are denser and with more defined boundaries. Cystic fibrous mastopathy may be accompanied by enlargement of the axillary or supraclavicular lymph nodes. There are frequent cases when cystic fibrous lumps that appear in the mammary glands do not cause concern.
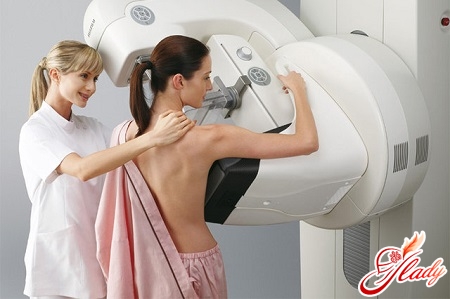
Diagnostic Methods
Early diagnosis of mastopathy is notpresents difficulties. Neoplasms are detected already during external examination and palpation (probing). The most informative and accurate way to diagnose pathological elements is a special method of X-ray analysis, that is, mammography. It records neoplasms starting from a size of 2-3 mm. If there is discharge from the nipples, a ductographic examination is carried out (a type of mammography). In cases of detection of a nodular form of mastopathy or suspicion of a malignant tumor, a puncture is taken for cytological examination. Some cases require hormonal studies (determination of the level of estrogens, progesterone, prolactin) and a biopsy of mammary gland tissue.
What can lead to the development of mastopathy
Mastopathy as a disease has been known for over a hundred years,but the ideas about the mechanism of its occurrence are mainly probabilistic. There is a whole range of reasons and factors that cause the appearance of cystic or fibrous tissues in the mammary glands. The main cause of the disease is considered to be hormonal imbalances in the body. The activity of the endocrine glands is such a subtle and complex mechanism that it can be disrupted by any processes occurring with deviations from the norm. Pathological disorders in the thyroid gland, diseases of the genitals and liver have a particularly strong influence. The activity of the mammary glands is provided by 15 different hormones. The mammary glands react sensitively to any deviation from the hormonal balance in the body. Fatty tissue of the breast is able to actively capture and accumulate hormonal substances. Diseases of the thyroid gland caused by imbalance in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, and accompanying metabolic disorders, diabetes and obesity increase the risk of developing fibrocystic diseases. Liver and biliary tract diseases are dangerous, which are accompanied by lipid and hormonal metabolism disorders and lead to hormonal disruptions. Cystic fibrous mastopathy occurs against the background of decreased immunity, chronic stress, increased mental and physical overload, hypothermia, unbalanced nutrition, smoking. Mastopathy develops especially often in the presence of chronic and acute gynecological diseases accompanied by hormonal production disorders. Often, pathologies in the mammary glands are noted after termination of pregnancy, late childbirth, uncontrolled use of contraceptives, some medications, especially hormonal and antidepressants. The onset of the disease can be provoked by hereditary predisposition, neuroses and depressions, multiple or single injuries, especially with deep damage.
Or maybe the parasites are to blame?
It is often said that mastopathyarises from parasitic lesions, for example, trichinella. This theory is supported by the fact that there are many known cases of mastopathy in children. The mammary glands are derivatives of the sweat glands, under the influence of certain factors the body begins to use the mammary glands to place unnecessary, pathologically harmful organisms there: microbes, fungi, worms. In the circular-longitudinal muscle fibers of the skin of the nipple and around it, bumps appear - evidence of the presence of trichinella larvae. It is from there that liquids can come out, including purulent ones. The mammary gland is densely permeated with closed networks of lymphocapillaries, through which trichinella larvae freely penetrate the body and can live in both the circulatory and lymphatic systems, freely migrating to any organ. In a closed network of lymphocapillaries, they gather into dense formations - conglomerates. The body, trying to isolate them, envelops them with fibrous tissue - this is how fibroadenoma appears. Trichinella are able to clog blood capillaries, then the liquid part of the blood seeps into the surrounding tissues, and the body builds a defense from the fibrous membrane - a cyst appears. These processes can occur singly or simultaneously and cause the development of fibrocystic mastopathy.
Mastopathy: self-treatment is excluded
Treatment of mastopathy is carried out in a comprehensive manner, withusing various methods, the combination of which is determined by many factors. In addition to the examination results, the patient's age, concomitant diseases, physiological development features and much more are of great importance. The basis of successful treatment is the elimination of the causes that led to the disease. This is the normalization of the endocrine glands, restoration of hormonal levels and metabolism, cure of existing diseases, stopping the formation of new seals, reducing pain. In the early stages of cystic and fibrous-diffuse mastopathy, not burdened by gynecological and endocrine diseases, therapy is mainly symptomatic. Homeopathic remedies are successfully used for treatment, having virtually no contraindications and restrictions on the duration of use. They slow down the formation of new and the growth of existing foci of mastopathy and reduce pain and swelling of the mammary glands. The most frequently prescribed medications are herbal preparations, herbal infusions and herbal teas that normalize metabolism, accelerate the removal of toxins and have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. External agents in the form of applications or compresses help relieve pain. Hormonal drugs have been used in the treatment of cystic fibrosis relatively recently, but they have already proven their effectiveness in slowing down pathological changes in breast tissue. These drugs have also proven effective in the late stages of diffuse mastopathy. Based on the results of a blood test, agents with different mechanisms and directions of action are selected: suppressive estrogens, slowing down the synthesis of the pituitary hormone prolactin and others. It turned out that hormonal contraceptives have a therapeutic and prophylactic effect. They contain gestagens and estrogens in ratios that help smooth out the instability of the hormonal background of the menstrual cycle. Nodular mastopathy at the initial stages can be treated with conservative methods. In advanced cases, excision of the altered tissues is required. However, even in this case, it is necessary to continue treatment.









