Cervical erosion is quite commona common disease associated with a disorder of the mucous membrane - that is, the epithelial covering of the cervix. This pathology occurs in 15% of women under 45 years of age. As a rule, erosion is detected during a routine gynecological examination. The doctor can easily distinguish the altered area from the surrounding healthy tissues by its pink-red color and characteristic granularity.
What is the difference between the usual erosion of the cervix from the congenital?
Congenital erosion of the cervix is considereda natural process occurring in the body of a young woman or girl. The uterus is the main organ of the female reproductive system, consisting of 3 main parts: the cervix, the isthmus and the body of the uterus. The cervix looks like a cylinder with a canal inside that connects it to the uterine cavity. The cervical canal (i.e. the cervical canal) is lined from the inside with a thin layer of unique integumentary tissue called columnar epithelium. This tissue protects against bacteria, physical and chemical damage. There are 2 types of epithelium: cylindrical - inside the cervix, and flat - outside. Initially, in a newborn girl, the cylindrical epithelium is located on the outside. However, with age, it gradually moves inward during normal physiological development. There are often cases when this process slows down, due to which a woman retains the condition of the cervix, like that of girls. This is influenced by several reasons: age, heredity, hormonal background. When such a pathology is detected, the doctor makes a diagnosis of congenital erosion.
Erosion: will we treat?
In most cases, congenital erosion of the cervixdoes not require treatment, since it goes away on its own after a hormonal shake-up. As a rule, this happens during pregnancy, puberty in girls, or after childbirth. Natural processes occur in the body that bring the cervix to a normal state. Therefore, do not be surprised if the doctor says that it is better not to touch the erosion before childbirth. It does not pose any danger to the fetus, and during pregnancy it most often resolves. Of the methods for treating congenital erosion, cauterization is considered the roughest. It is extremely undesirable to use such treatment before childbirth, since it can negatively affect the elasticity of the cervix and the process of its opening. And as a result of cauterization, these natural moments are disrupted. When such a phenomenon in a woman is not accompanied by an inflammatory process or other infections or diseases, it is enough to be monitored by a gynecologist every year. If inflammation or infection is detected, the doctor will conduct the necessary examination, after which he will prescribe the appropriate treatment. In addition to examination and consultation with a doctor, you should regularly take a culture and smear for infections (chlamydia, ureaplasma, HPV, mycoplasma, etc.) and vaginal flora. But the main procedure today that allows for accurate diagnostics is examination of the cervix under a microscope, that is, colposcopy. It allows you to see an accurate clinical picture. Pregnant women who have HPV should be especially careful, since erosion may degenerate. In this case, treatment of erosion is postponed until the birth of the child, it is monitored and the safest way to treat infections is offered. The fact is that infections can cause much more harm to both the mother and the child than prenatal elimination of congenital cervical erosion.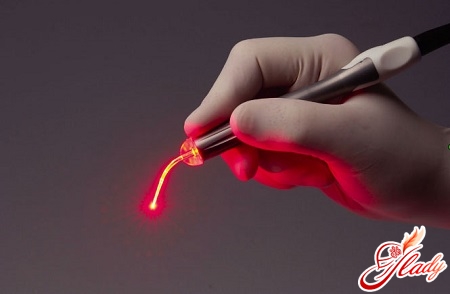
Methods of treatment
Today, doctors offer many methods for treating cervical diseases, including:
- Medications. The use of antibacterial drugs (tetracycline ointment, synthamycin emulsion, etc.), as well as agents that promote faster healing (rosehip oil, sea buckthorn oil, etc.), is now considered an outdated and ineffective method of treatment.
- Chemical removal of erosion. It is used if there are condylomas or only superficial tissues are affected. When pathological processes affect the deeper layers, the chemical drug partially affects the affected tissue, as a result of which erosion remains at the same place or progresses.
- Diathermocoagulation (electrocoagulation). The method is used only to treat erosion in women giving birth, since it promotes the formation of scars that constrict the cervical canal, which can lead to a rupture or serious damage to the cervix during childbirth.
- The use of liquid nitrogen - cryotherapy.This is a rather gentle and painless method that does not contribute to the formation of scars. The depth of penetration of the substance is sufficient only for the treatment of minor superficial lesions of the cervix and the removal of condylomas. The procedure is not performed in the presence of deep or serious damage. The effectiveness of the method is 54.96%. It is prescribed to women who have not given birth.
- Laser therapy. This is an effective modern method of treatment. During the procedure, the affected tissue is simultaneously removed, the bleeding stops. The method is painless and safe, it is possible to use it for nulliparous women, because it allows you to remove the existing damages with high accuracy.
- Radioknife - radio wave surgery.The procedure using radio waves is considered the most effective and gentle surgical technique. The mechanism of action of the radio knife is based on the energy of radio waves. The main advantage is that it cuts off (does not burn!) the damaged area, after which it can be sent for histological examination and a more precise diagnosis. This technique is a safe method, since the device not only removes tissue, but also stops bleeding that has begun as a result of surgery. The method is suitable for different women, including those who are planning to conceive in the future.
- Excision of the cervix. When the results of the biopsy show malignant formation, treatment should be continued with the oncologist. Treatment is successful in most cases, especially if the problem is found at an early stage of development. The operation can be performed using a radio-knife.
Sometimes erosion does not resolve in timepuberty, nor during pregnancy and childbirth, developing into a more serious pathology. In this case, you cannot delay treatment, otherwise the consequences can be very sad.