
Pertussis is an acute infectious disease,accompanied by severe attacks of spasmodic cough. In this disease, it is very important to determine the exact diagnosis. Diagnosis of whooping cough from the first day of the disease is almost impossible, and children are usually treated for a long time from bronchitis, tracheitis and ARVI. The source of this infection is only people - children who have become ill with atypical and typical forms of whooping cough, and healthy bacterial carriers. The most dangerous are patients in the initial stage of the disease. This infection is transmitted only by airborne droplets. In susceptible people, when in contact with a patient, the disease develops at a frequency of up to 90%. Most often, children of pre-school age fall ill. More than half of cases of the disease in young children occurs in connection with the insufficiency of maternal immunity and the absence of transplacental transmission of specific antibodies. In addition, there was a slight increase in incidence in the fall and winter. Pertussis stick, getting into the body by airborne droplets, is attached to the walls of the respiratory tract, causing there first light inflammatory processes (runny nose, reddening and sore throat, a slight cough). But the main and more severe signs of pertussis appear only after 10-14 days, when bacteria throw into the lumen of the bronchi and into the blood a large amount of their toxin. This leads to irritation not only of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, but also of the central nervous system. That's why children who get pertussis become very moody, sleep badly, their appetite is disturbed.
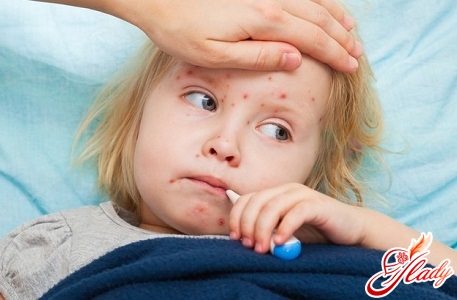
Pertussis: symptoms of each period of the disease
The period from the moment of penetration into the bodyinfection before the first symptoms of the disease (incubation period) can be from 6 to 20 days, but usually 7 days. The disease usually lasts for 6-8 weeks. Distinguish the following periods of the disease: the catarrhal period, the paroxysmal (or spasmodic) period, the period of reverse development (or resolution), and the period of recovery. Catarrhal Period Usually lasts 1-2 weeks. It flows in different ways and does not have any specific features. Symptoms of this period are: a mild cough, runny nose and a slight increase in body temperature. The child can have copious viscous discharge from the nose of the mucous nature. Body temperature can either increase slightly or remain normal, but in very severe cases it can also rise to 38-39 ° C. The severity of the disease also affects the severity of intoxication - from a slight malaise, irritability, anxiety and a decrease in appetite to a significant violation of the patient's overall well-being. During this period, cough is the main symptom of whooping cough. Cough is dry and with the intake of symptomatic drugs does not decrease, by the evening it intensifies and acquires the character of attacks. The catarrhal period in mild cases lasts 11-14 days, and in the most severe course - up to 8 days.  Paroxysmal (spasmodic) period Coughintensifies and becomes more frequent. A characteristic feature of this period is the appearance of repeated series of 5-10 cough shocks during one exhalation, followed by a sudden and intense breath, which is accompanied by a wheezing sound. There are other signs of this period: the child's face turns red or becomes cyanotic, the tongue hangs, the eyes roll out, saliva appears, the neck swells around the neck. Some children during the attacks there is an involuntary eruption of urine and feces, there may be convulsions and fainting. The attack ends with a large amount of thick, viscous mucus, sometimes even with vomiting. Severe attacks of cough can continue until the child does not get a viscous mucus, which violates the patency of the airways. Vomiting in this case refers to the typical signs of the disease. At this stage of the disease, the combination of coughing and vomiting is so characteristic that it is always necessary to suspect whooping cough in these cases, even if there is no wheezing after a cough. Cough very exhausting the child, he becomes frightened and alert. Cough can provoke sneezing, swallowing, physical activity, offering of drinking or eating, as well as sudden light, strong sudden noise, excitement or fright of the child. In the intervals between coughing episodes, children do not make the impression of seriously ill patients and feel quite satisfactory. They can safely play, be interested in others. All children feel the approach of a fit of coughing approach: the elders complain of a scratch behind the breastbone, a sore throat, the younger begin to cry, lose interest in toys, run to the mother, become restless. The number of attacks of cough depends on the severity of the disease. So, with mild pertussis, the number of attacks is 8-10 times a day, without vomiting. The overall well-being of the child is good. With pertussis of medium severity, the number of coughing attacks reaches up to 15 times a day, usually accompanied by vomiting. Between the attacks, the child's well-being improves, but does not completely normalize: the child refuses to eat, remains sluggish, sleeps badly, becomes moody. The face becomes puffy, the eyelids are edematous, hemorrhages appear on the conjunctiva. With severe pertussis, the number of coughing attacks can exceed 20-25 times a day. Oxygen deficiency develops, the skin becomes pale, a bluish tint of the nasolabial triangle appears. A tear and ulcer on the tongue of the tongue may appear due to strain and trauma to the lower incisors. In very serious cases, there may be a disorder of cerebral circulation, loss of consciousness, convulsions, a violation of the rhythm of breathing, which usually pass during the recovery period. In the absence of timely treatment, the spasmodic period lasts from 2 to 8 weeks and even more. By the end of this period, the number of cough attacks decreases, they become milder, and the disease passes into the next period. The period of reverse development (resolution) and recovery lasts from 2 to 4 weeks. Coughing attacks become rare, without vomiting. The child carries them much easier, his overall well-being and condition improves. The recovery period can last from 2 to 6 months. At this time, there is still weakness, irritability, increased excitability, susceptibility of children to other infections. In case of illness with other respiratory infections, for example, ARVI, cough may resume.
Paroxysmal (spasmodic) period Coughintensifies and becomes more frequent. A characteristic feature of this period is the appearance of repeated series of 5-10 cough shocks during one exhalation, followed by a sudden and intense breath, which is accompanied by a wheezing sound. There are other signs of this period: the child's face turns red or becomes cyanotic, the tongue hangs, the eyes roll out, saliva appears, the neck swells around the neck. Some children during the attacks there is an involuntary eruption of urine and feces, there may be convulsions and fainting. The attack ends with a large amount of thick, viscous mucus, sometimes even with vomiting. Severe attacks of cough can continue until the child does not get a viscous mucus, which violates the patency of the airways. Vomiting in this case refers to the typical signs of the disease. At this stage of the disease, the combination of coughing and vomiting is so characteristic that it is always necessary to suspect whooping cough in these cases, even if there is no wheezing after a cough. Cough very exhausting the child, he becomes frightened and alert. Cough can provoke sneezing, swallowing, physical activity, offering of drinking or eating, as well as sudden light, strong sudden noise, excitement or fright of the child. In the intervals between coughing episodes, children do not make the impression of seriously ill patients and feel quite satisfactory. They can safely play, be interested in others. All children feel the approach of a fit of coughing approach: the elders complain of a scratch behind the breastbone, a sore throat, the younger begin to cry, lose interest in toys, run to the mother, become restless. The number of attacks of cough depends on the severity of the disease. So, with mild pertussis, the number of attacks is 8-10 times a day, without vomiting. The overall well-being of the child is good. With pertussis of medium severity, the number of coughing attacks reaches up to 15 times a day, usually accompanied by vomiting. Between the attacks, the child's well-being improves, but does not completely normalize: the child refuses to eat, remains sluggish, sleeps badly, becomes moody. The face becomes puffy, the eyelids are edematous, hemorrhages appear on the conjunctiva. With severe pertussis, the number of coughing attacks can exceed 20-25 times a day. Oxygen deficiency develops, the skin becomes pale, a bluish tint of the nasolabial triangle appears. A tear and ulcer on the tongue of the tongue may appear due to strain and trauma to the lower incisors. In very serious cases, there may be a disorder of cerebral circulation, loss of consciousness, convulsions, a violation of the rhythm of breathing, which usually pass during the recovery period. In the absence of timely treatment, the spasmodic period lasts from 2 to 8 weeks and even more. By the end of this period, the number of cough attacks decreases, they become milder, and the disease passes into the next period. The period of reverse development (resolution) and recovery lasts from 2 to 4 weeks. Coughing attacks become rare, without vomiting. The child carries them much easier, his overall well-being and condition improves. The recovery period can last from 2 to 6 months. At this time, there is still weakness, irritability, increased excitability, susceptibility of children to other infections. In case of illness with other respiratory infections, for example, ARVI, cough may resume. 
Complications of pertussis
In young children whooping coughmuch heavier than older children. The incubation period decreases, the catarrhal period also lasts less, and the convulsive period becomes longer. Convulsive cough in many cases is absent, but there are bouts of anxiety, screaming, sneezing. The child can take the fetal position. There are often delays in breathing, which can last from 30 seconds to 2 minutes, and even stop breathing. They can occur outside the attack, during an attack and even in a dream. In the youngest children, vomiting can be caused by regurgitation. Very frequent complications of whooping cough in young children are disorders of cerebral circulation with paralysis, disorders of psychomotor development, bronchitis. The most common complication of whooping cough is pneumonia, which is caused by a pertussis or a secondary bacterial infection. 90% of deaths among children under 3 years are due to pneumonia. There may also be an exacerbation of tuberculosis. Other complications of pertussis may be acute laryngitis with stenosis of the larynx, bronchiolitis, encephalopathy, rupture of the diaphragm, inguinal or umbilical hernia, prolapse of the rectum. In adults, complications are rare. In vaccinated children, the disease occurs only in mild form, without complications and consequences, most often in an erased (atypical) form. 
Treatment of whooping cough in children
Children with moderate to severe diseaseshould be treated only in a hospital. It is very important to follow the regime of keeping and feeding sick children. It is necessary to eliminate all external stimuli, provide the child with a calm environment, to enable him to engage in quiet games. The room of a sick child should be frequently and well ventilated, install a humidifier in it. Or at least arrange containers with water, hang wet towels. If the child has a normal body temperature, then you can walk with him, but always avoid contact with other children. In summer, you can walk at any time, in winter - with wind and air temperature not lower than 12 ° C. The nutrition of the child should be full, fractional and sparing for cooking. It is important for breastfed children to maintain natural feeding by increasing the number of feedings and reducing the single milk volume. The same should be done with artificial feeding. A child after vomiting must be fed. During illness it is necessary to provide the child with enough liquid. In addition, you should exclude food in the dry, as it provokes coughing attacks, irritating the back wall of the pharynx. Treatment in the initial period of whooping cough consists in the use of antibiotics, since at this stage they can still suppress the development of the pathogen, and even a complete cure can occur even without the transition of the disease to the next stage. If the next stage has already come and there is a spasmodic cough, then antibiotics can no longer effectively affect the pertussis. That's why antibiotics are not prescribed in the second period of the disease. Treatment of whooping cough with fresh air and the use of antibiotics is not limited. There are many medications that help with coughing, but there is not one of them that can significantly alleviate the course of the disease. The choice of a specific drug for the treatment of whooping cough is a doctor's business. You should know that if the medicine prescribed by the doctor does not help from the point of view of the parents of the sick child, this does not mean that it is not advisable to take it. Most expectorants dilute sputum. The child can cough less, but the probability of complications in this disease will be significantly reduced, since it is the thick, viscous mucus that breaks the patency of the bronchi, which is the cause of the development of pneumonia. Pertussis toxins also cause allergic reactions to the entire body of the child, so antiallergic agents may be used for treatment. The doctor may prescribe antihistamines and calcium preparations, which also have anti-allergic effect. To dilute thick sputum, inhalation of proteolytic enzymes can be prescribed, but only for children from 3 years of age.
Preventive measures
The most reliable preventive measure for pertussisis the creation of immunity by vaccination. Vaccination is carried out according to the calendar of mandatory vaccinations with DTP vaccine. Vaccinations begin to be made to children from the age of three months, together with diphtheria and tetanus. The vaccine is transferred quite heavily, the child after the vaccination experiences an increase in body temperature, malaise, decreased appetite. The grafted children are also sick with whooping cough, but it is much easier, so the diagnosis of whooping cough is put in dozens of times less often than this disease actually occurs. He who has become ill with pertussis is isolated for 25 days. Children who are in contact with pertussis patients, especially in the first year of life, and unvaccinated before the age of 2, are injected with donor normal immunoglobulin. In a children's institution, when a patient with pertussis is registered, quarantine is imposed on children within 14 days from the date of isolation of the patient. The doctor must visit the sick child at home 1-2 times a week if pertussis is suspected, and when it is confirmed - depending on the condition of the patient. Each case of the disease is reported to the children's institution, which is visited by the child, and SES. Children under 7 years in contact with the patient, and children under the age of one year in contact with the patient, are separated for 14 days from the date of isolation of the patient. If the patient is not isolated, then in this case the duration of the quarantine is increased to 25 days from the appearance of signs of the disease of the first patient. Children over the age of 7 years (with pertussis) and children older than 1 year (with paracottus), adults are not subject to separation, but they should be followed by medical observation within 14 days, and if they continue to communicate with a pertussis patient, the observation can last longer. The peculiarity of whooping cough is the complete absence of innate immunity, so even a newborn can get this disease. But after treatment, a very persistent immunity is produced, which persists throughout life. Thus, whooping cough is a rather dangerous infectious disease, which every person can get sick. And if the above symptoms have appeared, treatment should be started as soon as possible. But do not self-medicate. If suspected pertussis should immediately consult a doctor who, after laboratory tests can either confirm the diagnosis, or exclude whooping cough. Symptoms that are characteristic of pertussis may also be symptoms of another disease. Therefore, only the doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. In time, the prescribed treatment can prevent the development of various complications that often occur with whooping cough. And, of course, do not forget about preventive measures, in time to make children vaccinated.









