
Whooping cough is an acute infectious diseasea disease accompanied by severe attacks of spasmodic cough. In this disease, it is very important to determine the exact diagnosis. It is almost impossible to diagnose whooping cough from the first day of the disease, and children usually undergo treatment for bronchitis, tracheitis and acute respiratory viral infections for a long time. The source of this infection is only a person - children who have fallen ill with atypical and typical forms of whooping cough, and healthy carriers of bacteria. The most dangerous are patients in the initial stage of the disease. This infection is transmitted only by airborne droplets. In susceptible people, upon contact with a patient, the disease develops with a frequency of up to 90%. Most often, preschool children get sick. More than half of the cases of the disease in young children occur due to insufficient maternal immunity and the absence of transplacental transmission of specific antibodies. In addition, some increase in the incidence of the disease is noted in the fall and winter. The whooping cough bacillus, having entered the body by airborne droplets, attaches to the walls of the respiratory tract, causing mild inflammatory processes there at first (runny nose, redness and sore throat, slight cough). But the main and more severe signs of whooping cough appear only after 10-14 days, when the bacteria release a large amount of their toxin into the lumen of the bronchi and into the blood. This leads to irritation of not only the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, but also the central nervous system. That is why children who have fallen ill with whooping cough become very capricious, sleep poorly, and have a disturbed appetite.
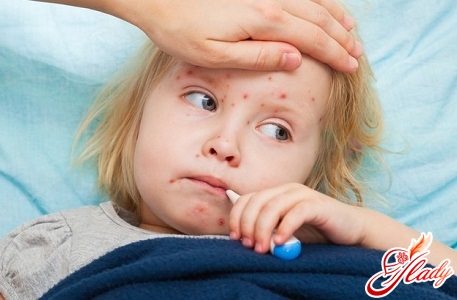
Pertussis: symptoms of each period of the disease
The period from the moment of penetration into the bodyinfection before the first symptoms of the disease appear (incubation period) can be from 6 to 20 days, but is usually 7 days. The disease usually lasts for 6-8 weeks. The following periods of the disease are distinguished: catarrhal period, paroxysmal (or spasmodic) period, period of reverse development (or resolution) and recovery period. Catarrhal period Usually lasts 1-2 weeks. It proceeds differently and does not have any specific features. Symptoms of this period are: mild cough, runny nose and a slight increase in body temperature. The child may have profuse viscous mucous discharge from the nose. Body temperature may either increase slightly or remain normal, but in very severe cases it may rise to 38-39ºС. The severity of the disease also depends on the severity of the disease - from slight malaise, irritability, anxiety and loss of appetite to a significant deterioration in the general well-being of the patient. During this period, cough is the main symptom of whooping cough. The cough is dry and does not decrease with symptomatic medications, and intensifies towards evening and takes on the character of attacks. The catarrhal period in mild cases lasts 11-14 days, and in the most severe cases - up to 8 days. Paroxysmal (spasmodic) period Coughусиливается и учащается. Характерной особенностью этого периода является появление повторных серий из 5-10 кашлевых толчков на протяжении одного выдоха, затем следует внезапный и интенсивный вдох, который сопровождается свистящим звуком. Существуют и другие признаки этого периода: лицо ребенка краснеет или становится синюшным, язык свисает, глаза выкатываются, появляется слюнотечение, на шее набухают вены. У некоторых детей во время приступов происходит непроизвольное извержение мочи и кала, могут наблюдаться судороги и обмороки. Завершается приступ выделением большого количества густой, вязкой слизи, иногда даже с рвотой. Тяжелые приступы кашля могут продолжаться до тех пор, пока у ребенка не выделится вязкая слизь, нарушающая проходимость дыхательных путей. Рвота в этом случае относится к типичным признакам заболевания. На данном этапе заболевания сочетание приступов кашля с рвотой является настолько характерным, что коклюш необходимо подозревать в этих случаях всегда, даже если отсутствует свистящий вдох после кашля. Кашель очень изнуряет ребенка, он становится напуганным и настороженным. Кашель может спровоцировать чихание, глотание, физическая нагрузка, предложение питья или еды, а также резкий свет, сильный внезапный шум, волнение или испуг ребенка. В промежутках между приступами кашля дети не производят впечатления тяжелобольных и чувствуют себя вполне удовлетворительно. Они могут спокойно играть, интересоваться окружающим. Все дети чувствуют приближение приступа кашля: старшие жалуются на царапанье за грудиной, першение в горле, младшие начинают плакать, теряют интерес к игрушкам, бегут к матери, становятся беспокойными. Количество приступов кашля зависит от тяжести заболевания. Так, при легкой форме коклюша количество приступов составляет 8-10 раз в сутки, без рвоты. Общее самочувствие ребенка при этом хорошее. При коклюше средней тяжести количество приступов кашля достигает до 15 раз в сутки, сопровождаются они обычно рвотой. Между приступами самочувствие ребенка улучшается, но полностью не нормализуется: ребенок отказывается от еды, остается вялым, плохо спит, становится капризным. Лицо становится одутловатым, веки отечными, появляются кровоизлияния на конъюнктиве. При коклюше тяжелой формы количество приступов кашля может превышать 20-25 раз в сутки. Развивается кислородная недостаточность, кожные покровы становятся бледными, появляется синюшный оттенок носогубного треугольника. Может появиться надрыв и язва на уздечке языка из-за напряжения и травмы о нижние резцы. В очень тяжелых случаях может возникнуть нарушение мозгового кровообращения, потеря сознания, судороги, нарушение ритма дыхания, которые в период выздоровления обычно проходят. При отсутствии своевременного лечения спазматический период длится от 2 до 8 недель и даже более. К концу этого периода количество приступов кашля уменьшается, они становятся мягче, и заболевание переходит в следующий период. Период обратного развития (разрешения) и выздоровления Длится от 2 до 4 недель. Приступы кашля становятся редкими, без рвоты. Ребенок переносит их гораздо легче, улучшается его общее самочувствие и состояние. Период выздоровления может длиться от 2 до 6 месяцев. В это время сохраняется еще слабость, раздражительность, повышенная возбудимость, восприимчивость детей к другим инфекциям. При заболевании другими респираторными инфекциями, например, ОРВИ, кашель может возобновиться.
Paroxysmal (spasmodic) period Coughусиливается и учащается. Характерной особенностью этого периода является появление повторных серий из 5-10 кашлевых толчков на протяжении одного выдоха, затем следует внезапный и интенсивный вдох, который сопровождается свистящим звуком. Существуют и другие признаки этого периода: лицо ребенка краснеет или становится синюшным, язык свисает, глаза выкатываются, появляется слюнотечение, на шее набухают вены. У некоторых детей во время приступов происходит непроизвольное извержение мочи и кала, могут наблюдаться судороги и обмороки. Завершается приступ выделением большого количества густой, вязкой слизи, иногда даже с рвотой. Тяжелые приступы кашля могут продолжаться до тех пор, пока у ребенка не выделится вязкая слизь, нарушающая проходимость дыхательных путей. Рвота в этом случае относится к типичным признакам заболевания. На данном этапе заболевания сочетание приступов кашля с рвотой является настолько характерным, что коклюш необходимо подозревать в этих случаях всегда, даже если отсутствует свистящий вдох после кашля. Кашель очень изнуряет ребенка, он становится напуганным и настороженным. Кашель может спровоцировать чихание, глотание, физическая нагрузка, предложение питья или еды, а также резкий свет, сильный внезапный шум, волнение или испуг ребенка. В промежутках между приступами кашля дети не производят впечатления тяжелобольных и чувствуют себя вполне удовлетворительно. Они могут спокойно играть, интересоваться окружающим. Все дети чувствуют приближение приступа кашля: старшие жалуются на царапанье за грудиной, першение в горле, младшие начинают плакать, теряют интерес к игрушкам, бегут к матери, становятся беспокойными. Количество приступов кашля зависит от тяжести заболевания. Так, при легкой форме коклюша количество приступов составляет 8-10 раз в сутки, без рвоты. Общее самочувствие ребенка при этом хорошее. При коклюше средней тяжести количество приступов кашля достигает до 15 раз в сутки, сопровождаются они обычно рвотой. Между приступами самочувствие ребенка улучшается, но полностью не нормализуется: ребенок отказывается от еды, остается вялым, плохо спит, становится капризным. Лицо становится одутловатым, веки отечными, появляются кровоизлияния на конъюнктиве. При коклюше тяжелой формы количество приступов кашля может превышать 20-25 раз в сутки. Развивается кислородная недостаточность, кожные покровы становятся бледными, появляется синюшный оттенок носогубного треугольника. Может появиться надрыв и язва на уздечке языка из-за напряжения и травмы о нижние резцы. В очень тяжелых случаях может возникнуть нарушение мозгового кровообращения, потеря сознания, судороги, нарушение ритма дыхания, которые в период выздоровления обычно проходят. При отсутствии своевременного лечения спазматический период длится от 2 до 8 недель и даже более. К концу этого периода количество приступов кашля уменьшается, они становятся мягче, и заболевание переходит в следующий период. Период обратного развития (разрешения) и выздоровления Длится от 2 до 4 недель. Приступы кашля становятся редкими, без рвоты. Ребенок переносит их гораздо легче, улучшается его общее самочувствие и состояние. Период выздоровления может длиться от 2 до 6 месяцев. В это время сохраняется еще слабость, раздражительность, повышенная возбудимость, восприимчивость детей к другим инфекциям. При заболевании другими респираторными инфекциями, например, ОРВИ, кашель может возобновиться. 
Complications of pertussis
In young children, whooping cough occursmuch more severe than in older children. The incubation period decreases, the catarrhal period also lasts less, and the convulsive period becomes longer. Convulsive cough is absent in many cases, but attacks of anxiety, screaming, sneezing are observed. The child may assume the fetal position. Often there are pauses in breathing, which can last from 30 seconds to 2 minutes, and even respiratory arrest. They can occur outside of an attack, during an attack, and even in sleep. In the smallest children, regurgitation may occur instead of vomiting. Very common complications of whooping cough in young children are cerebrovascular accidents with paralysis, psychomotor development disorders, bronchitis. The most common complication of whooping cough is pneumonia, which is caused by the whooping cough bacillus or a secondary bacterial infection. 90% of deaths among children under 3 years of age are caused by pneumonia. An exacerbation of tuberculosis may also occur. Other complications of whooping cough may include acute laryngitis with laryngeal stenosis, bronchiolitis, encephalopathy, diaphragmatic rupture, inguinal or umbilical hernia, rectal prolapse. In adults, complications are rare. In vaccinated children, the disease occurs only in a mild form, without complications and consequences, most often in an erased (atypical) form.
Treatment of whooping cough in children
Children with moderate to severe diseaseshould be treated only in hospital. It is very important to follow the regime of keeping and feeding sick children. It is necessary to eliminate all external irritants, provide the child with a calm environment, give him the opportunity to play quietly. The room of a sick child should be frequently and well ventilated, install a humidifier in it. Or at least place vessels with water, hang wet towels. If the child has a normal body temperature, then you can walk with him, but be sure to avoid contact with other children. In summer you can walk at any time, in winter - in calm weather and air temperature not lower than 12ºС. The child's nutrition should be complete, fractional and gentle in preparation. It is important for infants to maintain natural feeding, increasing the number of feedings and reducing the one-time volume of milk. The same should be done with artificial feeding. The child must be fed after vomiting. During illness, it is necessary to provide the child with a sufficient amount of liquid. In addition, dry food should be excluded, as it provokes coughing fits, irritating the back of the throat. Treatment in the initial period of whooping cough consists of the use of antibiotics, as at this stage they can still suppress the development of the pathogen, and even a complete cure may occur without the disease progressing to the next stage. If the next stage has already arrived and a spasmodic cough has appeared, then antibiotics will no longer be able to effectively affect the whooping cough bacillus. That is why antibiotics are not prescribed in the second period of the disease. Treatment of whooping cough is not limited to fresh air and the use of antibiotics. There are many drugs that help with cough, but none of them can significantly alleviate the course of the disease. The choice of a specific drug for the treatment of whooping cough is a doctor's business. You should know that if the drug prescribed by the doctor does not help from the point of view of the parents of a sick child, this does not mean that it is inappropriate to take it. Most expectorants thin the sputum. The child may not cough less, but the likelihood of complications with this disease will be significantly reduced, since it is thick, viscous mucus that disrupts the bronchial patency, causing pneumonia. Whooping cough toxins also cause allergies in the child's entire body, so antiallergic drugs can be used in treatment. The doctor can prescribe antihistamines and calcium preparations, which also have an antiallergic effect. To thin thick sputum, inhalations of proteolytic enzymes can be prescribed, but only for children over 3 years of age.
Preventive measures
The most reliable preventive measure for whooping coughis the creation of immunity by vaccination. Vaccination is carried out according to the calendar of mandatory vaccinations with the DPT vaccine. Vaccinations are started for children from the age of three months along with diphtheria and tetanus. The vaccine is tolerated rather hard, after vaccination the child experiences a fever, malaise, loss of appetite. Vaccinated children also get whooping cough, but much easier, therefore the diagnosis of whooping cough is made tens of times less often than this disease actually occurs. A person with whooping cough is isolated for 25 days. Children who have been in contact with a patient with whooping cough, especially in the first year of life, and unvaccinated up to 2 years are given donor normal immunoglobulin. In a child care facility, when a patient with whooping cough is registered, children are quarantined for 14 days from the day of isolation of the patient. A doctor should visit a sick child at home 1-2 times a week if whooping cough is suspected, and if it is confirmed - depending on the patient's condition. Each case of the disease is reported to the child care facility the child attends and the SES. Children under 7 years of age who are in contact with the patient and children under one year of age who are in contact with the patient are separated for 14 days from the day the patient is isolated. If the patient is not isolated, the quarantine period is increased to 25 days from the onset of signs of the disease in the first patient. Children over 7 years of age (with whooping cough) and children over 1 year of age (with parakoklyush), adults are not subject to separation, but they must be under medical supervision for 14 days, and if they continue to communicate with the patient with whooping cough, the supervision can last even longer. The peculiarity of whooping cough is the complete absence of innate immunity to it, so even a newborn can get this disease. But after treatment, very strong immunity is developed, which lasts throughout life. Thus, whooping cough is a rather dangerous infectious disease that anyone can get. And if the above symptoms appear, treatment should be started as soon as possible. But you should not self-medicate. If you suspect whooping cough, you should immediately consult a doctor who, after conducting laboratory tests, can either confirm the diagnosis or exclude whooping cough. Symptoms characteristic of whooping cough may also be symptoms of another disease. Therefore, only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Timely prescribed treatment can prevent the development of various complications that often occur with whooping cough. And, of course, do not forget about preventive measures, vaccinating children on time.









