
HPV (or human papillomavirus) isa general name for viruses that includes DNA viruses that affect epithelial cells. This group of viruses includes more than 150 different representatives and causes various diseases of the skin and mucous membranes. More than 30 types of viruses cause the development of genital infections. The greatest danger of this virus is that it is oncogenic and can cause various tumors and squamous cell cancer. The human papilloma virus poses the greatest danger to women. Men do not suffer from the consequences as much, so they are called carriers.
General information and risks of infection
The most common route of infection issexual intercourse. Moreover, the risk of infection is directly proportional to the number of sexual partners: the more partners, the greater the likelihood of infection. Modern medicine believes that infection is possible through everyday life. This issue has not yet been fully studied: it is very difficult to determine the time of infection, because the incubation period can last up to several years, depending on the state of the immune system, and the carriage is asymptomatic, a person may not even suspect for a long time that he is a carrier. You can get infected through a kiss (if the papillomas are located on the lips). In medical practice, cases of infection of newborns from infected mothers during childbirth have been registered, but the risk of such infection is estimated as low and is 3%. The amount of the virus depends on the immunity of the mucous membranes and skin. With a decrease in the latter, the virus actively begins to affect human cells, accumulating on a small area of the skin. Having accumulated in sufficient volume, the virus begins to change the function of epithelial cells. Cells begin to divide uncontrollably. This causes the growth of a skin area and the appearance of various formations (papillomas and condylomas) on the human body. Depending on the type of virus, the diseases it causes will differ. Therefore, the symptoms will also differ.
Skin formations
Warts are raised, rounded orirregularly shaped, compacted, painless skin lesions of small size. They are usually located in the most traumatic places - on the elbows, fingers, knees. Sometimes they can disappear unexpectedly. They cause aesthetic discomfort, especially in women. Papillomas (the most common sign of HPV) are soft, round, flesh-colored (sometimes closer to brown) formations that are attached either to a wide base or to a stalk. Most often they are located on the face, armpits, neck, in the genital area. An important sign is that papillomas grow quickly: both their size and number increase. Pointed condylomas are peculiar warts that appear on the mucous membranes and genitals. Favorite places for their appearance include the perineum, the mucous membrane of the labia, and the vagina in women. In men - the skin of the foreskin and the head of the penis. The number of papillomas can vary - from 1 to several hundred in a small area. In medical practice, there is also such a concept as confluent pointed condylomas - the fusion of several pointed condylomas into a single whole, resembling cauliflower in appearance. Bowenoid papulosis - rashes in the form of compacted plaques of yellowish, pink or white color on the skin of the genitals. Sometimes it develops into skin cancer. Flat condylomas of the cervix (dysplasia of the cervix) are a precancerous condition, very often degenerating into a cancerous tumor. Visually, it is a colony of papillae covered with keratinized epithelium on top. In order not to miss this disease, women need to visit a gynecologist every six months.
Course of infection
In the process of infectious infection, 3 are distinguishedforms of human papillomavirus: latent, subclinical and clinical. Latent form - absence of any signs of the disease. The virus can be detected only by testing for the presence of HPV DNA in the human body. Subclinical form of infection - signs of the disease in the form of small condylomas or atypical changes in the cervix. But they are so small that they are not visible to the naked eye. They are detected only by special research methods. Clinical form - skin lesions of all types visible to the naked eye. According to research, the human papillomavirus is found in the body of 70-90% of people of reproductive age. But in most cases, the human immune system fights the disease on its own, and the virus does not develop beyond the latent form. This mainly occurs at a young age (up to 30 years), and it takes up to 2 years to expel the virus from the body. At a more mature age, the human body has a much more difficult time coping with the virus.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis and treatment of HPV in women is carried out bygynecologist. Diagnostics begins with the clarification of complaints (even with a subclinical form, women may complain of discomfort during intercourse) and a general examination. For women, it will be mandatory to examine the cervix and vagina using speculums, cytological examination or Pap smear (PAP test) - analysis of cells taken from the cervix and cervical canal, colposcopy - visual examination of the epithelium of the cervix using a special device - a colposcope. If oncology is suspected, a piece of cervical tissue or a fragment of a condyloma can be taken for biopsy (diagnosis), as this allows for the detection of oncology at early stages. One of the most reliable research methods is PCR diagnostics (polymerase chain reaction) - DNA diagnostics of the virus for oncogenicity. But the method has a serious drawback - a false positive result is possible. Today, the most accurate diagnostic method is the Digene test, which allows not only to detect the virus, but also to determine its DNA affiliation and degree of malignancy. Nowadays, the combination of the Digene test and the PAP test is the diagnostic standard for diagnosing cervical pathologies in women.
Methods of treatment
Because in our time they have not yet been createddrugs, the action of which could remove the virus from the human body, modern treatment is aimed at eliminating the clinical manifestations of the disease. It includes 3 stages: destruction of papillomatous foci (destructive methods), immunological treatment, general strengthening therapy. Destructive methods. Depending on what disease the virus caused, the medical tactics also differ. The main methods of treatment are physical (cryo-, laser-, electrotherapy, radio wave surgery), surgical and chemical. Immunological treatment includes stimulation of cellular immunity with the help of antiviral agents and agents for stimulation of general human immunity. Such drugs include interferons, amixin, isoprinosine, podophyllin, cycloferon, neovir, lilyupid, immunomax, gepon, etc. It should be noted that self-medication is unacceptable. Any drug must be prescribed by a doctor. Among non-medicinal means, ozone therapy (the use of ozone solutions to stimulate the immune system) can be noted. Not all people achieve a positive result from the use of this group of drugs. And none of the drug treatment methods guarantees a complete cure for the disease. General tonic therapy. This includes vitamin therapy, sedatives (stress has a very negative effect on the immune system), general tonic therapy, and normalization of metabolism.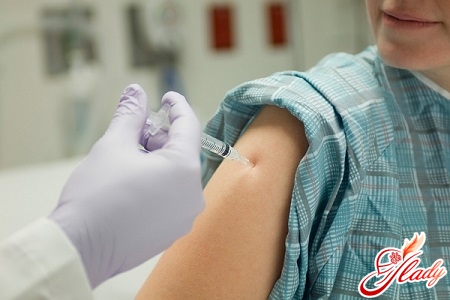
Preventive measures
Since in most cases thisThe disease is transmitted sexually, unprotected sex should be avoided. However, a condom will not provide you with 100% protection (since it may not cover the entire area of the affected skin), although it will significantly reduce the risk of infection. You should limit the number of casual sexual contacts. The only 100% method of preventing the disease is sexual intercourse with one partner and mutual fidelity throughout life. Vaccines have been developed to prevent cervical cancer and severe forms of dysplasia in women caused by HPV. According to health data, vaccination has been clinically proven to protect against several types of papillomavirus that can cause cervical cancer. According to research, women are most often infected in the first 3 years from the onset of sexual activity, and the vaccination is most effective if it is done before the onset of sexual activity. In this regard, as a rule, it is prescribed in advance, at 12-13 years of age. In Russia today there are two vaccines against the human papilloma virus: Cervarix and Gardasil. The latter protects against several other types of the virus that can cause genital warts, as well as against viruses responsible for penile cancer in men. The course consists of three vaccinations according to the 0-1-6 month schedule. The vaccine is administered into the deltoid muscle of the shoulder. Cervarix is used only for women aged 10-25. Gardasil is also administered to men. The cost of vaccinations at the beginning of 2014 was about 5,000 rubles per dose. Of course, it is up to you to decide whether it is expensive or not, whether it is worth getting vaccinated or not. But, according to official data, 18 women under 40 die from cervical cancer every day in Russia.









