Pregnancy is the happiest time inlife of almost every woman. But unfortunately, sometimes pregnancy is marred by problems. And one of the most terrible problems is a frozen pregnancy. After all, what could be worse for a woman who was preparing to become a happy mother than to find out that her baby is not destined to be born? The woman was pregnant and happy in the morning, and just one doctor's appointment plunged her into real hell. Every woman has heard something about a frozen pregnancy, but did not go into details if she had not encountered it herself. But if the doctor made this terrifying verdict, the woman - whether she wants it or not - is forced to find out more about a frozen pregnancy. That is why we have collected all the necessary information, paying special attention to curettage, which is simply impossible to do without.
Pregnancy is the happiest time inlife of almost every woman. But unfortunately, sometimes pregnancy is marred by problems. And one of the most terrible problems is a frozen pregnancy. After all, what could be worse for a woman who was preparing to become a happy mother than to find out that her baby is not destined to be born? The woman was pregnant and happy in the morning, and just one doctor's appointment plunged her into real hell. Every woman has heard something about a frozen pregnancy, but did not go into details if she had not encountered it herself. But if the doctor made this terrifying verdict, the woman - whether she wants it or not - is forced to find out more about a frozen pregnancy. That is why we have collected all the necessary information, paying special attention to curettage, which is simply impossible to do without.
What is a dead pregnancy?
First of all, you need to have an ideaabout what a frozen pregnancy is. And why pregnancy freezes at all. This is what doctors call a phenomenon in which, for one reason or another, the embryo stops developing and, naturally, dies. In no case should a frozen pregnancy be confused with the lagging development of the fetus - in the second case, the future baby, subject to timely and proper treatment, has every chance of being born healthy. Most often, trouble happens in the earliest stages - more than 85% of all cases of frozen pregnancy occur in the first trimester (that is, in the first 3 months after conception). The remaining 15% occur in the second trimester of pregnancy. Well, if the misfortune occurred in the last months, doctors do not talk about a frozen pregnancy, but about intrauterine fetal death. Of course, no woman can independently understand that the pregnancy has frozen - even a doctor will need some time and a series of tests. But a woman may suspect something is wrong if she discovers the following symptoms:
- Toxicosis
If you had toxicosis and it happened suddenly,a couple of days, disappeared - this is a reason to think about whether everything is okay with your pregnancy. Toxicosis develops under the influence of hormones responsible for the normal course of pregnancy. In most cases, toxicosis weakens by the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy, but this happens gradually, day after day. If one fine morning you, who yesterday suffered from severe toxicosis, get up and realize that you feel great and there is no hint of nausea, immediately tell your gynecologist about it. It is unlikely, but there is still a risk that the pregnancy has frozen, the hormone level has dropped sharply, as a result of which, in fact, the toxicosis has stopped.
- Mammary gland
Almost all women have mammary glandsundergo changes already at the beginning of pregnancy - they become rough, slightly increase in size - the action of the same hormones. And if the pregnancy stops developing and the level of hormones decreases, the mammary glands will quickly return to their pre-pregnancy state.
- Discharge from the vagina
It is absolutely unacceptable to ignorebloody vaginal discharge, no matter how intense it is. Of course, in most cases, doctors eliminate the cause of the bleeding and save the baby, but not in the case of a frozen pregnancy.
Diagnosis of frozen pregnancy
"By eye" a frozen pregnancy is notdiagnosed - to make such a diagnosis, the gynecologist carefully examines the woman, because in this case, an error is simply unacceptable. The following types of diagnostics are used for this:
- Manual research
Most often frozen in the early stagespregnancy is discovered completely by accident - during a routine examination, the gynecologist notices that the size of the uterus does not correspond to the expected gestational age. But this factor alone is not enough to confidently say that the pregnancy has been frozen - it is necessary to rule out a delay in fetal development.
- Blood test
Many doctors consider it necessary to prescribe a blood test to determine the level of certain hormones - this often helps to clarify the situation.
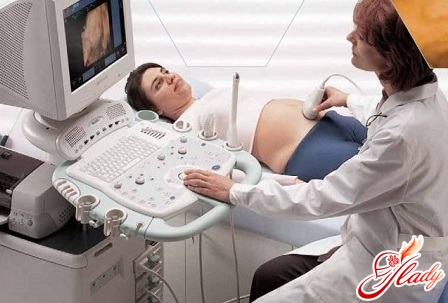
- Ultrasonography
And a mandatory diagnostic procedure -ultrasound examination of the uterus. The doctor will examine the uterine cavity, the fertilized egg, adequately assess their size and find out whether the fetus has a heartbeat. The reliability of the ultrasound examination is very high - the probability of error is no more than one percent.
Embryo removal
If the frozen pregnancy is confirmed,it is necessary to save the woman - if the fertilized egg remains in the uterus, complications will begin very soon - from severe inflammatory processes to general blood poisoning - sepsis. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to remove the fertilized egg from the uterine cavity - you should not hope for a spontaneous miscarriage, and it does not guarantee that everything will go smoothly. Doctors usually act in the case of a frozen pregnancy as follows:
- Medicamentous interruption of a stunted pregnancy
If the pregnancy period was very short,the doctor can try to get rid of the fertilized egg without surgery, using special medications - similar to a medical abortion. The woman takes pills with a high content of hormones that provoke a miscarriage. However, there is no guarantee that the fetus will come out completely and there will be no need to clean the uterine cavity.
- Scraping
The most common and reliable way to removeembryo - uterine cavity curettage. The doctor surgically cleans the uterus from the embryo and placenta. This is what we will now tell you about in more detail.
Scraping of the uterus cavity
Despite the fact that scraping isthe procedure is far from new and very widespread, many women are panicky afraid of it. As a rule, fear arises from ignorance of what will happen and the expectation of pain. There is no special preparation before this procedure. All that is required from a woman is not to eat the day before the procedure and remove pubic hair. As a rule, curettage is almost always done under general anesthesia, so the anesthesiologist will talk to the woman in advance. In addition, the woman will definitely be thoroughly examined again by a gynecologist. The fact is that conventional curettage has a number of contraindications, such as: some acute inflammatory processes of the uterus and appendages, infectious diseases, suspicions of a violation of the integrity of the uterine mucosa. Of course, in these cases, it is necessary to get rid of the ovum, but the technique of curettage in this case will be slightly different. As mentioned above, most often the doctor performs curettage under general anesthesia - the woman lies down in a gynecological chair, the anesthesiologist administers a drug and the woman comes to in the ward. But if for one reason or another the use of general anesthesia is impossible, local anesthesia is used - the cervix and body of the uterus are injected with special drugs, as a result of which they lose sensitivity. Before the procedure, the doctor will necessarily treat the woman's external genitalia with a special iodine solution, and the vagina and cervix with medical alcohol to exclude the possibility of infection. In some cases, if the doctor overdoes the treatment, the woman may experience mild discomfort for several days. After this, the doctor will insert a special device into the vagina, with the help of which the cervix is expanded. Then, with the help of dilators, the open cervix is fixed in this position and the doctor proceeds directly to the removal of the ovum. To do this, he scrapes out the uterine mucosa using a curette, which most closely resembles a spoon. This procedure lasts an average of 15-20 minutes if everything goes smoothly, without complications.
Complications after curettage
Despite the fact that the scraping techniquethe uterine cavity is well-developed and is familiar to all doctors without exception, we must not forget that this is still a surgical intervention. This means that there is always a risk of developing certain complications.
- Perforation of the uterus wall
Perforation is damage to the integrityuterine walls. A very serious complication that can lead to serious problems, including the need for serious surgical intervention. Fortunately, this happens extremely rarely - less than 1% of all curettage cases.
- Bleeding
Sometimes curettage in case of a frozen pregnancymay result in bleeding. This phenomenon should never be ignored - immediately inform your doctor, even if the bleeding is not heavy. Otherwise, there is a high risk that blood clots will begin to accumulate in the uterine cavity. And this may lead to the need for repeated curettage. And you do not need iron deficiency anemia.
- Inflammatory processes
After curettage of the uterus, the mucous membraneis one big gaping wound. Therefore, it is very easy for any infection to penetrate into it. Carefully monitor your health - if your temperature rises, pain occurs, immediately tell your doctor.
- Adhesive processes
A more distant complication that can resultknow about yourself only after several years - these are adhesions in the pelvis. Pain, menstrual irregularities, and sometimes even secondary infertility - not the most pleasant consequences of the adhesion process.
Postoperative period
So, curettage after a frozen pregnancybehind - it's time for the postoperative period. The likelihood of developing various complications depends on how it proceeds - that's why doctors pay so much attention to it. The following indicators should be under special control:
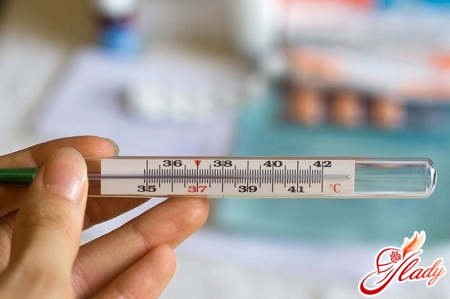
- Body temperature
In the first day after curettage it is possiblean increase in temperature to 37 - 37 and 5 degrees. But on the second and subsequent days, the body temperature should be normal. And even the slightest increase is an alarm bell indicating that an inflammatory process is possible.
- Vaginal discharge
Curettage in case of frozen pregnancy -the procedure is quite traumatic, so you can't do without blood. But remember that there should not be heavy bleeding, so if your pad is soaked through faster than an hour, there is a reason to worry. In addition, you need to pay attention to the smell of discharge - if it becomes unpleasant, you can suspect an infection. As a rule, if everything goes according to plan and without complications, the woman will not be kept in the hospital for a long time - in a few days she will already be home. But you should not relax there either - keep your health under strict control for at least two or three weeks. On the 14th day after curettage, be sure to visit a gynecologist. Firstly, an examination is necessary, which will allow you to understand whether the uterus has contracted. Secondly, you cannot do without an ultrasound examination - the doctor must make sure that there are no pieces of the ovum or fetal membranes left in the uterine cavity. In addition, in some cases, a woman may need therapy to help bring her hormonal balance back into order. And the main thing you need to do is to come to terms with this tragedy and learn to live on. We recommend reading: