Nowadays, probably every womanheard of such a serious and dangerous disease as cervical cancer, which has one of the highest mortality rates in the world. However, not everyone knows that the causes of this malignant tumor in the female body are the entry of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is a DNA virus that leads to uncontrolled cell division, resulting in genital warts, papillomas and other external symptoms of infection on the skin. This virus is especially dangerous for women, as it can provoke cervical cancer. According to statistics, this happens in 80% of cases. There are more than a hundred different types of HPV, 35 of which affect the mucous membrane of the genitals. Some of them provoke the appearance of warts and other neoplasms, others can cause cancer. Types of human papillomavirus are classified by the degree of oncological risk: for example, there are viruses with a low probability of oncogenic risk (6, 11), medium risk (31, 33) and high risk (16, 18, 45). Papilloma is a benign tumor, its main element is a connective tissue papilla containing vessels and covered with epithelium. Papillomas develop from squamous epithelium and can appear in the oral cavity, on the genitals, and also on the mucous membrane of the nose. Human papillomavirus is more common in women than in men. Basically, HPV is transmitted to humans through sexual contact. However, there are other ways of infection: through household items, when shaking hands. There is a risk of catching this infection in public places, for example, when visiting a swimming pool or a bathhouse. The virus penetrates a person through small wounds and even cracks in the skin. Most often, the symptoms of infection with the human papillomavirus do not appear for a long time, its incubation period can last on average 3 months. The human papillomavirus is especially dangerous for women, since it can remain undetected for a long time and is accidentally discovered during a gynecological examination.
Nowadays, probably every womanheard of such a serious and dangerous disease as cervical cancer, which has one of the highest mortality rates in the world. However, not everyone knows that the causes of this malignant tumor in the female body are the entry of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is a DNA virus that leads to uncontrolled cell division, resulting in genital warts, papillomas and other external symptoms of infection on the skin. This virus is especially dangerous for women, as it can provoke cervical cancer. According to statistics, this happens in 80% of cases. There are more than a hundred different types of HPV, 35 of which affect the mucous membrane of the genitals. Some of them provoke the appearance of warts and other neoplasms, others can cause cancer. Types of human papillomavirus are classified by the degree of oncological risk: for example, there are viruses with a low probability of oncogenic risk (6, 11), medium risk (31, 33) and high risk (16, 18, 45). Papilloma is a benign tumor, its main element is a connective tissue papilla containing vessels and covered with epithelium. Papillomas develop from squamous epithelium and can appear in the oral cavity, on the genitals, and also on the mucous membrane of the nose. Human papillomavirus is more common in women than in men. Basically, HPV is transmitted to humans through sexual contact. However, there are other ways of infection: through household items, when shaking hands. There is a risk of catching this infection in public places, for example, when visiting a swimming pool or a bathhouse. The virus penetrates a person through small wounds and even cracks in the skin. Most often, the symptoms of infection with the human papillomavirus do not appear for a long time, its incubation period can last on average 3 months. The human papillomavirus is especially dangerous for women, since it can remain undetected for a long time and is accidentally discovered during a gynecological examination.


Factors that increase the likelihood of a papillomavirus infection in women
Let's take a closer look at which women are at risk for developing the human papilloma virus. The following factors may contribute to this.
A woman often changes her sexual partners.
Tobacco smoking.
Decreased immunity.
Early sexual life.
If a woman had sexual intercourse with a partner who had contact with a carrier of HPV (she had condyloma, cervical cancer).
Alcohol abuse.
Metabolic disorders.
The presence of gynecological diseases.
Frequent visiting of a sauna, a bath, a pool (it is places of the raised humidity).
Presence of gastritis.


Manifestation of HPV in women
In women, HPV often manifests itself in the following way.
The appearance of genital warts, whichare a type of condylomas and look like small growths with jagged edges that are located on a wide base. Often, condylomas do not manifest any symptoms, except for itching in the area of the external genitalia and pain during urination or sexual intercourse. Pointed condylomas (another name is genital warts) are small growths that are the color of human skin, appearing most often around the anus or on the genitals. These growths first appear only a few months after infection. Genital warts are localized mainly on the cervix, in its canal, in the vagina, around the anus. The appearance of genital warts on the cervix or in the cervical canal significantly increases the likelihood of the occurrence and development of a malignant tumor of the cervix.
Cervical dysplasia (when the uterus is inprecancerous condition) - a disease caused by the high-risk papillomavirus (HPV types 16 and 18). It is not diagnosed during a routine gynecological examination. It is detected as a result of cytological and histological examinations.
Flat condyloma of the cervix is the most commona dangerous manifestation of the human papilloma virus, since its appearance means that the viral infection has been in the woman's body for a long time and has long been causing changes in the epithelial cells of the cervix.
Cervical cancer is a malignant neoplasm caused by the human papillomavirus (mainly types 16 and 18).
In addition to the above-mentioned manifestations of papillomavirus infection, women also experience other neoplasms that are caused by various types of human papillomavirus.
Plantar wart.A wart is a benign neoplasm on human skin caused by different types of HPV. Warts are usually rounded skin elevations that occur due to strong proliferation of the superficial layers of the epithelium. Plantar warts form in areas of strong shoe pressure, the risk of their occurrence increases in women with increased sweating. They are usually very painful, hard and cause significant discomfort when walking.
Keratopapilloma is a keratinizedpapilloma that has a spherical, conical or multi-lobular shape. It can be of different colors: brown, flesh-colored or blue-burgundy. It appears mainly on the neck, under the arms, and on the face.
Fibropapilloma is a benign tumor,which are nodular formations protruding above the skin surface. Fibropapilloma can be of different sizes and shapes. Formations can be brownish or pale pink. Most often they appear on the head and body.
Seborrheic wart - benignan epithelial tumor that can develop over several years. It is predominantly brown in color. Over time, its surface becomes covered with cracks, and it itself increases in size and can reach 5-6 cm in diameter. It is usually localized on the neck, face, and limbs.
Flat papilloma.The causes of this type of papillomas are HPV types 3 and 10. Flat papillomas are smooth, flat, flesh-colored bumps of a polygonal or round shape. Symptoms of a flat papilloma include redness, itching, and inflammation of the affected area of the skin.
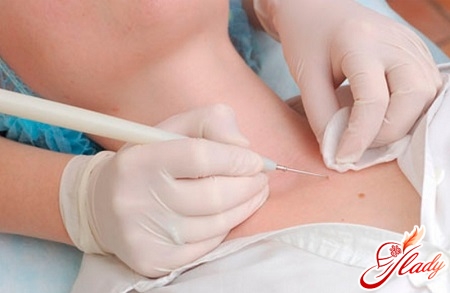


Diagnosis of human papillomavirus in women
The following methods are used to diagnose this infection in women.
Examination by a doctor-gynecologist. The cervix is examined by the doctor with the help of a gynecological mirror for the presence of genital warts and warts.
Colposcopy.This method allows you to carefully examine the surface of the cervix using a colposcope - a special device that can magnify the image many times. With its help, the doctor conducts certain tests that help to see the places affected by HPV: a test with acetic acid (pointed condylomas appear under the influence of a 3% solution of acetic acid), tests with Lugol's solution. They are painless and very effective.
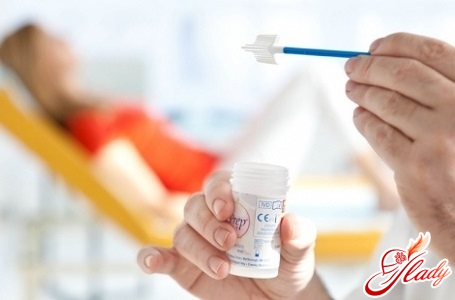
Cervical scraping examination (other(names - Pap test or cytological smear). It is carried out by examining under a microscope smears taken from the mucous membrane of the cervix and cervical canal. If an infection is present, the cervical cell changes. In addition, the cytological examination method helps to detect cervical cancer in the initial phase, even before the absence of signs of this disease, visible to the naked eye.
Digene-test for today hashigh sensitivity among all methods of diagnosis of HPV. Its technology is based on the phenomenon of hybridization (which means DNA binding to the RNA probe) and capture of the resulting hybrid on the solid phase with monoclonal antibodies. After that, the hybrid is bound by antibodies labeled with the enzyme. The test is completed by chemiluminescence. The material for the study can be tissue obtained from a biopsy, scraping of epithelial cells taken from the vagina or cervical canal.
Cervical biopsy is a procedure in which a sample of tissue from the cervix is taken and examined under a microscope.
With the polymerase chain reaction, the DNA of the human papillomavirus is determined in the body by taking a scraping from the uterine cervical canal.
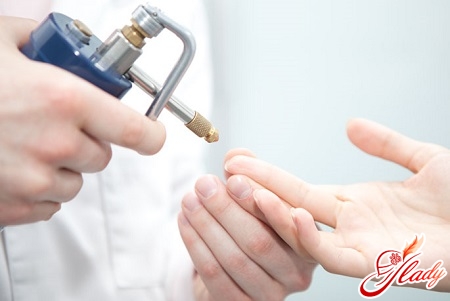


Treatment of HPV in Women
Currently, HPV treatment is carried outvarious methods, but it is impossible to get rid of it completely. All treatment of this virus is reduced to the elimination of its clinical and subclinical manifestations. In each specific situation, treatment is selected individually. Treatment of papillomavirus in women should be carried out simultaneously in several directions.
- Local treatment. Provides removal of altered epithelial sites by different methods: traditional surgical procedure, cryodestruction, radio wave method, diathermocoagulation, laser radiation, chemical removal.
Surgical treatment means removing the affected areas with a scalpel. It is used mainly in the presence of extensive lesions of tissues, with suspicion of malignant formations.
Cryodestruction involves the freezing of neoplasms with the help of liquid nitrogen.
Peaked condylomas are eliminated using radio wave coagulation. A radio wave knife is used for this.
Diathermocoagulation is a procedure for excision of genital warts with high frequency radiation or an electron knife.
Laser radiation - eliminationneoplasms with a laser. It is the only procedure suitable for pregnant women to remove condylomas. But treatment with this procedure does not exclude the formation of scars.
Chemical removal refers to the elimination of formations by the application of acid-containing preparations to them by the application method.
- Purpose of antiviral drugs. It is carried out for the purpose of conducting anti-relapse therapy, as well as during the acute phase of the disease. Such treatment is necessary because of the prevention of malignant neoplasm.
- The appointment of immunomodulators, vitamins and minerals. Treatment of the human papilloma virus, thus, helps to restore and strengthen the immune system, which is important in the fight against HPV.



Human papillomavirus during pregnancy
This infection is very dangerous duringpregnancy, both for the expectant mother and for the child, the reasons for its danger - a high probability of transmitting the virus to the baby during childbirth or during intrauterine development. Before planning a pregnancy, all women should be examined for the presence of HPV. If the virus is detected during the examination, doctors usually advise postponing the birth of the child and first treating the infection. In cases where the human papillomavirus is detected during pregnancy, doctors recommend postponing treatment until 28 weeks - all the organs of the future baby are already formed by this time and will not suffer from the negative effects of drugs. Women are not recommended to give birth on their own if the condylomas are in the vagina, because in this case the risk of infection of the child increases.

Prevention of papillomavirus in women
There are several areas of HPV prevention in women.
Use of a special prophylactic vaccine.Currently, there are two types of vaccines available in the trade network that are used to prevent cervical cancer and other genital cancers: Cervarix and Gardasil. It is worth noting that these vaccines are only used in healthy women, that is, in those who have not been diagnosed with the human papillomavirus.
Using condoms during sexual intercourse.
Refusal from smoking and excessive use of alcohol.
Increased immunity.
Regular visit to the gynecologist. Periodic visits to the doctor will help to detect human papillomavirus in women in the early stages of its manifestation, and this is the key to a more successful treatment.
No one is immune from HPV infection.However, following simple preventive measures will help reduce the risk of infection to a minimum. But if the human papilloma virus is found in your body, start timely treatment. Remember that in this case, you care not only about your health, but also about the health of your future children!
Comments
comments

Nowadays, probably every womanheard of such a serious and dangerous disease as cervical cancer, which has one of the highest mortality rates in the world. However, not everyone knows that the causes of this malignant tumor in the female body are the entry of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is a DNA virus that leads to uncontrolled cell division, resulting in genital warts, papillomas and other external symptoms of infection on the skin. This virus is especially dangerous for women, as it can provoke cervical cancer. According to statistics, this happens in 80% of cases. There are more than a hundred different types of HPV, 35 of which affect the mucous membrane of the genitals. Some of them provoke the appearance of warts and other neoplasms, others can cause cancer. Types of human papillomavirus are classified by the degree of oncological risk: for example, there are viruses with a low probability of oncogenic risk (6, 11), medium risk (31, 33) and high risk (16, 18, 45). Papilloma is a benign tumor, its main element is a connective tissue papilla containing vessels and covered with epithelium. Papillomas develop from squamous epithelium and can appear in the oral cavity, on the genitals, and also on the mucous membrane of the nose. Human papillomavirus is more common in women than in men. Basically, HPV is transmitted to humans through sexual contact. However, there are other ways of infection: through household items, when shaking hands. There is a risk of catching this infection in public places, for example, when visiting a swimming pool or a bathhouse. The virus penetrates a person through small wounds and even cracks in the skin. Most often, the symptoms of infection with the human papillomavirus do not appear for a long time, its incubation period can last on average 3 months. The human papillomavirus is especially dangerous for women, since it can remain undetected for a long time and is accidentally discovered during a gynecological examination.