
Today in modern societythe level of medical care is of great importance. There are many different diseases that are dangerous for humans. This group includes infections, injuries, hereditary pathology, cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the respiratory system and endocrine system and, of course, neoplasms. The latter can be benign and malignant. A special place among them is occupied by the so-called cysts, including those of the brain. The brain is the central organ that coordinates the activity of all systems. A brain cyst is a dangerous disease, but still benign, unlike cancer. The importance of this issue lies in the fact that cysts are often discovered by chance during medical examinations and tests. A person may not notice any symptoms or the disease itself for years, and cysts often do not manifest themselves externally. The difficulty of providing medical care in this case is also of great importance, because it is often necessary to resort to difficult operations on the brain. Let us consider in more detail what a brain cyst is, the main causes of this pathology, and how therapy is carried out.

Definition and etiology
Cyst — This is a cavity formed inголовном мозге, заполненная в большинстве случаев жидкостью. Это довольно распространенная патология, поражающая как взрослых, так и детей в любом возрасте. Иногда кисты возникают на мозговых оболочках в месте их слипания после перенесенного воспалительного процесса. Кисты можно обнаружить случайно при проведении магнитно-резонансной и компьютерной томографии. Киста может развиться вследствие перенесенного заболевания. Ее могут вызвать менингиты (воспаления оболочек головного мозга), энцефалиты (воспаления вещества головного мозга), травматические повреждения или воспалительные заболевания, перенесенные инсульты и операции. Развивается она не сразу, а постепенно. Киста головного мозга не относится к онкологическим болезням. В большинстве случаев они растут в течение нескольких лет. Симптомы отсутствуют, но если она имеет большие размеры, то это может вызвать сдавление коры головного мозга, мягких тканей, что нередко провоцирует появление неврологических симптомов. Классификация кист головного мозга Киста в голове может быть нескольких типов. В зависимости от типа ткани, из которой она развивается, выделяют следующие ее виды: арахноидальную, коллоидную, дермоидную, эпидермоидную и пинеальную. Рассмотрим более подробно каждую из них. Итак, арахноидальная киста головного мозга получила свое название от наименования оболочки головного мозга, где она развивается, — арахноидальной или паутинной. Она возникает после перенесенного кровоизлияния, травмы или воспалительного процесса. Она опасна тем, что при высоком давлении может сдавливать кору мозга. Поражает в основном детей и подростков преимущественно мужского пола. Коллоидная киста в отличие от предыдущей возникает в голове еще на стадии эмбриогенеза во время закладки нервной системы. При больших размерах она способствует ухудшению оттока спинномозговой жидкости из головного мозга, и развивается гидроцефалия (водянка мозга). Это требует обязательного хирургического вмешательства. Киста в голове может быть дермоидной, тогда она произрастает из клеток зачатка лица еще на стадии развития плода, нередко обнаруживается у детей до 10 лет. Следующий тип кисты — эпидермоидный. Отличие заключается в том, что клетки — ее предшественники — зачатки волос, кожи и ногтей. Удаляется она из головы хирургически. И последний тип — пинеальная. Образуется она в шишковидном теле примерно у 1-4 % пациентов с кистой. При развитии гидроцефалии она может вызвать сонливость, диплопию (двоение в глазах), дезориентацию, трудность поднятия взгляда вверх. Основные клинические симптомы Киста головного мозга на ранних стадиях развития никак себя не проявляет. Клинические симптомы практически отсутствуют. Основная причина их появления — это развитие осложнения и большие размеры. Киста может сдавливать окружающие ткани, при этом повышается давление. Когда оно становится больше внутричерепного, это может привести к следующим симптомам: появлению чувства распирания в голове, возникновению шума в ушах, головной боли, повышенной пульсации сосудов, зрительным нарушениям, в частности двоению в глазах и более серьезным последствиям, таким как парезы и параличи конечностей, онемению. Это возможно вследствие ущемления черепных нервов, которые расположены в головном мозге. Каждый из них отвечает за определенную часть тела, иннервируя ее. Большое значения имеет и то, что кисты могут расти. Происходит это более активно, если действует вредный или травмирующий фактор. Рост их можно контролировать с помощью магнитно-резонансной и компьютерной томографии. Как уже было сказано выше, арахноидальные кисты расположены на поверхности, то есть на мозговых оболочках. Рост ее может быть связан с повышением давления, сотрясениями мозга при уже имеющемся образовании и если продолжается воспаление (арахноидит). Киста может поражать и вещество головного мозга, тогда она называется внутримозговой. Растет она при продолжающемся патологическом или аутоиммунном процессе (рассеянный склероз, энцефаломиелит). Большое значение в качестве провоцирующего фактора играет нарушение кровообращения в результате микроинсультов. Все это способствует разрушению вещества головного мозга. 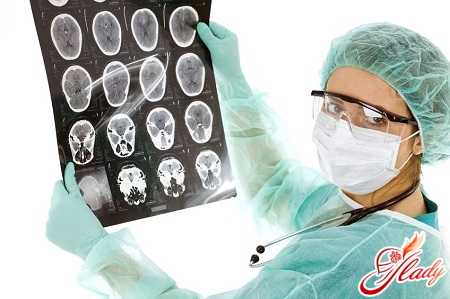 Basic principles of diagnosis of brain cystof the brain will manifest itself sooner or later, but you should not wait if symptoms appear. The reasons for its appearance can be very different. Diagnosis of a brain cyst includes, first of all, collecting anamnesis. A special place is occupied by the anamnesis of the current disease. It includes establishing the possible causes of this disease and symptoms. Establishing previously suffered diseases plays a major role, because a cyst can be their consequence. Of particular diagnostic importance is the presence in the anamnesis of previously suffered strokes, inflammatory diseases, for example, encephalitis or meningitis. A cyst can be a consequence of previously performed surgical interventions, the presence of concomitant pathology of autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. The next stage is the patient's complaints. They may be completely absent, and the consequences will be bad for the patient. The data of the external examination of the patient are also important. Much attention is paid to the nervous system and sense organs, since they are very often affected. The most important stage is conducting instrumental and laboratory tests. Instrumental and laboratory examination of the patient A cyst is easily detected by magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. This method is effective and reliable. MRI will help to identify the cyst itself, determine its exact size and location. To distinguish it from a tumor, you can use the method of intravenous administration of a contrast agent. It is important to remember that a tumor accumulates it, but a cyst does not. On the screen, it is depicted as a dark lesion with clear contours, the localization can be different. Doppler examination of the vessels of the brain and neck has found wide application. Impaired blood flow, narrowing of the vessels that supply the brain with oxygen (arteries) - all these are signs of a possible stroke and the appearance of a cyst. The cause of oxygen deficiency in the brain can be a disorder of the cardiovascular system. To exclude it, an ultrasound examination of the heart and adjacent large vessels is performed. Laboratory test results can also indicate symptoms and the presence of a cyst. The presence of elevated cholesterol in the blood, high coagulability - these are the causes of cerebral vascular occlusion. It is recommended to monitor blood pressure. Determining the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid is also of great importance.
Basic principles of diagnosis of brain cystof the brain will manifest itself sooner or later, but you should not wait if symptoms appear. The reasons for its appearance can be very different. Diagnosis of a brain cyst includes, first of all, collecting anamnesis. A special place is occupied by the anamnesis of the current disease. It includes establishing the possible causes of this disease and symptoms. Establishing previously suffered diseases plays a major role, because a cyst can be their consequence. Of particular diagnostic importance is the presence in the anamnesis of previously suffered strokes, inflammatory diseases, for example, encephalitis or meningitis. A cyst can be a consequence of previously performed surgical interventions, the presence of concomitant pathology of autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. The next stage is the patient's complaints. They may be completely absent, and the consequences will be bad for the patient. The data of the external examination of the patient are also important. Much attention is paid to the nervous system and sense organs, since they are very often affected. The most important stage is conducting instrumental and laboratory tests. Instrumental and laboratory examination of the patient A cyst is easily detected by magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. This method is effective and reliable. MRI will help to identify the cyst itself, determine its exact size and location. To distinguish it from a tumor, you can use the method of intravenous administration of a contrast agent. It is important to remember that a tumor accumulates it, but a cyst does not. On the screen, it is depicted as a dark lesion with clear contours, the localization can be different. Doppler examination of the vessels of the brain and neck has found wide application. Impaired blood flow, narrowing of the vessels that supply the brain with oxygen (arteries) - all these are signs of a possible stroke and the appearance of a cyst. The cause of oxygen deficiency in the brain can be a disorder of the cardiovascular system. To exclude it, an ultrasound examination of the heart and adjacent large vessels is performed. Laboratory test results can also indicate symptoms and the presence of a cyst. The presence of elevated cholesterol in the blood, high coagulability - these are the causes of cerebral vascular occlusion. It is recommended to monitor blood pressure. Determining the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid is also of great importance.
Treatment of the cyst of the brain
The cyst may require immediate treatment.In most cases, this is not required, especially if there are no complaints, clinical symptoms and the cyst does not increase in size. If it is actively growing and compressing the cerebral cortex, this is an indication for drug or even surgical intervention. Treatment is mainly aimed at treating the underlying disease that caused its formation. If it is arachnoiditis, then treatment necessarily includes the use of resorbable drugs such as caripain or longidaza. If there is a circulatory disorder, treatment includes reducing blood clotting by administering anticoagulants, lowering blood cholesterol levels and normalizing blood pressure (treatment with antihypertensive drugs). Treatment of the pathology will require the administration of nootropics, which promote the saturation of brain cells with oxygen and glucose, which is very important. Treatment that includes antioxidants is recommended. The latter increase the resistance of brain cells to high pressure. In case of dropsy and impaired outflow of intracerebral fluid, it is advisable to include furosemide in the treatment. If the cause of the disease is an infection, autoimmune pathology, then the treatment includes the prescription of immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs. Surgical treatment is possible. In this case, endoscopic operations are better suited.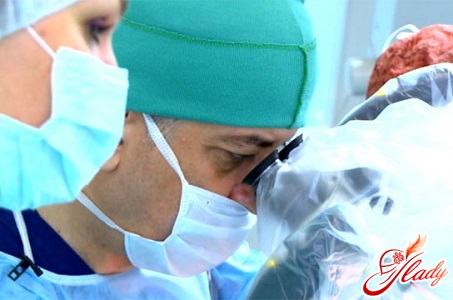
Cyst of the brain in children
As already mentioned above, this disease canmay also occur in children. But in this population group, the disease appears as a result of an infectious disease suffered by the mother during pregnancy. Often the cause may be birth trauma. Many viral infections can cause meningitis (inflammation of the meninges), untimely treatment of which leads to the development of cysts. The arachnoid type of process is formed more often. It is not necessary to exclude an intracerebral cyst (cerebral). The reasons for it are birth trauma as a result of unskilled assistance, a narrow pelvis of the mother, exostoses, and so on. They are also possible in adolescents. The location may be different: in the cerebellum, corpus callosum, brainstem, nuclei, hemispheres. The fluid replaces the lost (dead) part of the brain. In adults, there are other causes. Treatment of cysts in children is similar to that in adults.
Conclusion, conclusions, recommendations
Based on all of the above, we can concludethe conclusion that a cyst is a fluid-filled formation that can form in any area of the head. It should be distinguished from a tumor, which is an oncological pathology. The main causes of the disease are injuries, past illnesses, circulatory disorders, and maternal illnesses during pregnancy. Symptoms do not always appear, only in severe cases, with complications, or with large cystic formations. Complications such as hydrocephalus, paresis, and paralysis of the limbs, compression of the cortex, and the risk of cyst enlargement are very dangerous. Diagnostics includes collecting anamnesis, examination, determining complaints and main symptoms, and instrumental and laboratory examination of the patient. MRI or CT are most optimal. Treatment is not necessary in most cases. Therapy includes treating the underlying disease, eliminating the traumatic factor, and, in extreme cases, performing surgery. This pathology mostly affects children, as well as adolescents and adults, and more often men than women. Therefore, if you have the first symptoms, you should definitely see a doctor.









