
Today in modern societythe level of medical care is of great importance. There are many different diseases that are dangerous to humans. This group includes infections, trauma, hereditary pathology, cardiovascular diseases, respiratory and endocrine system diseases and, of course, neoplasms. The latter can be benign and malignant. A special place among them is occupied by so-called cysts, including the brain. The brain is the central organ that coordinates the activities of all systems. The brain cyst is a dangerous disease, but still benign, unlike cancer. The importance of this issue lies in the fact that often cysts are detected accidentally during medical examinations and examinations. The person for years can not notice any symptomatology and the disease itself, and cysts often do not appear externally. Of great importance is the difficulty of providing medical care in this case, because you often have to resort to difficult operations on the brain. Let us consider in more detail what the cyst of the brain is, the main causes of the onset of this pathology, and how the therapy is performed.

Definition and etiology
Cyst is a cavity formed in the headthe brain, filled with liquid in most cases. This is a fairly common pathology that affects both adults and children at any age. Sometimes cysts appear on the meninges in the place of their adhesion after the inflammatory process. Cysts can be detected by chance during magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. The cyst can develop as a result of the disease. It can cause meningitis (inflammation of the brain envelopes), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain substance), traumatic injuries or inflammatory diseases, suffered strokes and surgeries. It does not develop immediately, but gradually. The cyst of the brain does not belong to oncological diseases. In most cases, they grow for several years. Symptoms are absent, but if it is large, it can cause compression of the cerebral cortex, soft tissues, which often provokes the appearance of neurologic symptoms. Classification of cysts of the brain Cyst in the head can be of several types. Depending on the type of tissue from which it develops, its following types are distinguished: arachnoid, colloidal, dermoid, epidermoid and pineal. Let us consider in more detail each of them. So, the arachnoid cyst of the brain derives its name from the name of the brain envelope, where it develops - arachnoid or arachnoid. It occurs after a hemorrhage, an injury, or an inflammatory process. It is dangerous because at high pressure it can squeeze the cerebral cortex. It affects mainly children and adolescents predominantly male. The colloid cyst, unlike the previous one, occurs in the head even at the stage of embryogenesis during the laying of the nervous system. At large sizes, it helps to worsen the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the brain, and hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus) develops. This requires mandatory surgical intervention. The cyst in the head can be dermoid, then it grows from the cells of the rudimentary face even at the stage of fetal development, it is often found in children under 10 years old. The next type of cyst is epidermoid. The difference is that the cells - its predecessors - are the rudiments of hair, skin and nails. It is removed from the head surgically. And the last type is pineal. It is formed in the pineal body in approximately 1-4% of patients with a cyst. With the development of hydrocephalus, it can cause drowsiness, diplopia (double vision in the eyes), disorientation, difficulty in lifting the gaze upward. The main clinical symptoms of the cyst of the brain in the early stages of development does not manifest itself. Clinical symptoms are practically absent. The main reason for their appearance is the development of complications and large sizes. The cyst can squeeze the surrounding tissue, while increasing pressure. When it becomes more intracranial, it can lead to the following symptoms: the appearance of a feeling of raspiraniya in the head, the development of noise in the ears, headache, increased pulsation of the vessels, visual disturbances, particularly double vision and more serious consequences, such as paresis and paralysis of the limbs , numbness. This is possible due to the infringement of the cranial nerves, which are located in the brain. Each of them is responsible for a certain part of the body, innervating it. Of great importance is the fact that cysts can grow. This happens more actively if there is a harmful or traumatic factor. Their growth can be controlled by means of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. As already mentioned above, arachnoid cysts are located on the surface, that is, on the meninges. Its growth can be associated with increased blood pressure, concussions of the brain with an existing education and if inflammation continues (arachnoiditis). The cyst can also affect the brain substance, then it is called intracerebral. It grows with a continuing pathological or autoimmune process (multiple sclerosis, encephalomyelitis). Of great importance as a provoking factor is the disruption of blood circulation as a result of micro strokes. All this contributes to the destruction of the substance of the brain. 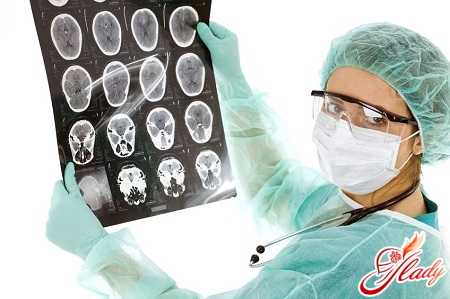 Basic principles of diagnosis of the cyst of the headthe brain will sooner or later manifest itself, but you do not need to wait for the symptoms to appear. The reasons for its appearance can be very different. Diagnosis of the cyst of the brain includes, in the first place, the collection of anamnesis. A special place is taken by the anamnesis of the present disease. It involves determining the possible causes of the onset of the disease and symptoms. An important role is played by the establishment of previously transmitted diseases, because the cyst can be their consequence. Particular diagnostic significance is the presence in the history of previously suffered strokes, inflammatory diseases, for example, encephalitis or meningitis. The cyst may be a consequence of previous surgical interventions, the presence of a concomitant pathology of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis. The next stage is the patient's complaints. They may be completely absent, and the consequences will be bad for the patient. Data of external examination of the patient is also important. Much attention is paid to the nervous system and sensory organs, since they are very often affected. The most important stage is carrying out instrumental and laboratory research. Instrumental and laboratory examination of the patient Cyst is easily detected when conducting magnetic resonance and computed tomography. This method is effective and reliable. MRI will help identify the cyst itself, determine its exact size and location. To distinguish it from the tumor, you can apply the method of intravenous contrast agent. It is important to remember that the tumor accumulates it, and the cyst does not. On the screen it is depicted in the form of a dark hearth with clear contours, the localization can be different. Doppler study of the vessels of the brain and neck was widely used. Violation of the blood flow, narrowing of the vessels that supply the brain with oxygen (arteries) - all these are signs of a possible stroke and the appearance of a cyst. The cause of oxygen deficiency of the brain may be a violation of the cardiovascular system. To exclude it, an ultrasound examination of the heart and adjacent large vessels. Symptoms and presence of cysts can also be indicated by laboratory data. The presence in the blood of high cholesterol, high coagulability - the cause of blockage of the vessels of the brain. It is recommended to monitor blood pressure. It is also important to determine the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Basic principles of diagnosis of the cyst of the headthe brain will sooner or later manifest itself, but you do not need to wait for the symptoms to appear. The reasons for its appearance can be very different. Diagnosis of the cyst of the brain includes, in the first place, the collection of anamnesis. A special place is taken by the anamnesis of the present disease. It involves determining the possible causes of the onset of the disease and symptoms. An important role is played by the establishment of previously transmitted diseases, because the cyst can be their consequence. Particular diagnostic significance is the presence in the history of previously suffered strokes, inflammatory diseases, for example, encephalitis or meningitis. The cyst may be a consequence of previous surgical interventions, the presence of a concomitant pathology of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis. The next stage is the patient's complaints. They may be completely absent, and the consequences will be bad for the patient. Data of external examination of the patient is also important. Much attention is paid to the nervous system and sensory organs, since they are very often affected. The most important stage is carrying out instrumental and laboratory research. Instrumental and laboratory examination of the patient Cyst is easily detected when conducting magnetic resonance and computed tomography. This method is effective and reliable. MRI will help identify the cyst itself, determine its exact size and location. To distinguish it from the tumor, you can apply the method of intravenous contrast agent. It is important to remember that the tumor accumulates it, and the cyst does not. On the screen it is depicted in the form of a dark hearth with clear contours, the localization can be different. Doppler study of the vessels of the brain and neck was widely used. Violation of the blood flow, narrowing of the vessels that supply the brain with oxygen (arteries) - all these are signs of a possible stroke and the appearance of a cyst. The cause of oxygen deficiency of the brain may be a violation of the cardiovascular system. To exclude it, an ultrasound examination of the heart and adjacent large vessels. Symptoms and presence of cysts can also be indicated by laboratory data. The presence in the blood of high cholesterol, high coagulability - the cause of blockage of the vessels of the brain. It is recommended to monitor blood pressure. It is also important to determine the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment of the cyst of the brain
A cyst may require immediate treatment. In most cases this is not required, especially if there are no complaints, the clinical symptoms and cyst does not increase in size. If it actively grows and squeezes the cerebral cortex - this is an indication for medication or even surgical intervention. The treatment is mainly aimed at treating the underlying disease that provoked her education. If this is arachnoiditis, the treatment necessarily includes the use of resorptive medications, such as caripain or longidase. If there is a violation of blood circulation, treatment includes a decrease in blood clotting due to the introduction of anticoagulants, lowering blood cholesterol and normalizing blood pressure (treatment with antihypertensive drugs). Treatment of pathology will require the appointment of nootropics, which contribute to the saturation of brain cells with oxygen and glucose, which is very important. Recommended treatment, including antioxidants. The latter increase the resistance of brain cells to high blood pressure. When dropsy and violation of the outflow of intracerebral fluid, it is advisable to include furosemide in the treatment. If the cause of the ailment is infection, autoimmune pathology, then treatment includes the appointment of immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs. Possible surgical treatment. In this case, endoscopic surgeries are best. 
Cyst of the brain in children
As already mentioned above, this ailment canarise and in children. But in this population, the disease appears as a result of a mother's infectious disease during pregnancy. Often, the cause may be in trauma. Many viral infections can cause meningitis (inflammation of the brain envelopes), untimely treatment of which leads to the development of cysts. Arachnoidal type of process is often formed. It is not necessary to exclude and intracerebral cyst (cerebral). Its causes are trauma at delivery as a result of unskilled help, a narrow pelvis of the mother, exostoses and so on. At teenagers they too are possible. The location can be different: in the cerebellum, corpus callosum, trunk, nuclei, hemispheres. The fluid replaces the lost (dead) part of the brain. Adults have other reasons. Treatment of cysts in children is similar to adults.
Conclusion, conclusions, recommendations
Based on the foregoing,the conclusion that a cyst is a formation filled with a liquid that can form in any area of the head. It must be distinguished from a tumor, which is an oncological pathology. The main causes of the illness: injuries, diseases, circulatory disorders, mother's diseases during pregnancy. Symptoms are not always manifested, only if there is a severe course, the presence of complications or with a huge amount of cystic education. Very serious complications, such as hydrocephalus, paresis and paralysis of the extremities, compression of the cortex and the threat of an increase in cysts. Diagnosis includes the collection of anamnesis, examination, identification of complaints and underlying symptoms, instrumental and laboratory examination of the patient. The most optimal use of MRI or CT. Treatment in most cases is not necessary. Therapy includes treatment of the underlying disease, elimination of the traumatic factor, in extreme cases - the operation. This pathology affects children, as well as adolescents and adults, more often than men, than women. Therefore, if you have the first symptoms, you should always consult a doctor.









