Today, molluscum contagiosumare classified as a form of skin dermatosis. Mollusks are considered a parasitic viral disease characterized by both local and general rashes on the mucous membranes and skin surface in the form of small spherical bubbles with a depression in the center. Contagious molluscum is a chronic disease. Causing damage to the skin, the infection can live in the body from 1 month to several years. Usually, rashes are noticed from 6 to 9 months. Contagious dermatosis is a purely human disease, neither animals nor birds carry it. Human infection occurs from contact of a healthy person with an already infected one. The causative agent of the disease is a virus related to smallpox. The virus multiplies in the cytoplasm of cells. The shape of the rash is rectangular or oval.

Causes of development of molluscum contagiosum
As already mentioned, the causative agent of thisThe cause of the disease is the molluscum contagiosum virus, which many experts classify as a smallpox virus. Modern medicine today does not allow us to completely get rid of the pathogen of this viral disease because it remains in the DNA structure. Of course, it is possible to avoid relapses of molluscum by strengthening the human immune system. As a result of a decrease in the immune system's protective response due to the effect of unfavorable factors, molluscum contagiosum is activated, due to which all sorts of clinical manifestations of this disease occur. The location of the skin lesion by the molluscum contagiosum virus depends on how the infection occurred. An adult usually becomes infected through sexual contact with a carrier of the virus, so the location of localization, of course, will be the genital (external) organs, the perineum, pubis, and possibly the lower abdomen and thighs (usually the inner surface). Molluscum contagiosum in children can affect any area of the skin, it is impossible to determine the place where it will appear, since in this case the infection occurs through everyday life (this situation is also suitable for adults who have a non-sexual infection). Most often, the development of the disease occurs when the human body is weakened as a result of some disease, which implies a very high risk of infection for a person with a weakened immune system. This disease can also develop in the presence of HIV infection (this situation usually occurs in adults who were infected through sexual contact). When the disease is introduced into human skin (in the cells of the epidermis), elementary bodies are formed (oval inclusions in the upper layer of the skin). As a result of the increase in size, the bodies of the mollusk become to the surface of the skin. From the outside, these rashes look like nodules with a granular mass inside. When merging, these neoplasms can occupy an area of skin with a diameter of 2-3 cm. Of course, they usually spread singly, but sometimes they can be in groups.
Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum
Infection with the virus usually occurs throughsexual contact, but there is also a household route of transmission of infection (using a sick person's towel). Very often, a swimming pool becomes the place of infection, especially for small children. It may take from several weeks to several months before neoplasms appear on the skin (on an area of skin where there is a tattoo, the latent state can reach 7 months). Clinical manifestations are dense nodules, in certain cases having a pearlescent shade, which are painless. Most often, these are single formations, which can then grow over a very large area of the skin. These nodules can have a wide variety of sizes, from a grain to a large pea (giant neoplasms can form, but in very rare situations). To open a nodule, just press on it with tweezers, and you will find a granular mass of white or slightly yellowish color, which contains many mollusc-like bodies. Large neoplasms have a depressed place with a small hole in the middle. There are cases of itching of the skin, characterized by a large presence of neoplasms. There is a high probability that another bacterial infection may join, which in turn will entail severe inflammation.
Diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum
The forms of molluscum contagiosum are distinguished by their development:
Usually this is enough to make a diagnosis.a routine consultation with a dermatologist, in rare cases, the contents of existing neoplasms are taken for analysis. In the absence of inflammatory processes of the skin located near the neoplasms, their limited size, as well as the presence of a depression in the middle of the neoplasm with a small hole through which a granular white mass begins to come out, it is quite easy to make the correct diagnosis. In the case of taking the contents of the neoplasm for examination under a microscope, one can observe the detection of keratinized cells in small quantities against the background of a very large number of mollusk-shaped bodies. Thanks to research, it can be argued that the formation of bodies occurs deep in the epithelium, and the filling of cells with the virus occurs due to their increase in size and the ability to displace its nucleus. The localization of molluscum neoplasms in children infected through household contact and adults with sexually transmitted infection differ markedly. In children, this is almost always the face, when cutaneous molluscum in adults most often affects the genitals, lower abdomen and anus. People often confuse this disease with the symptoms of chickenpox and varieties of syphilis, so it is imperative to consult a doctor who will prescribe treatment.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in children
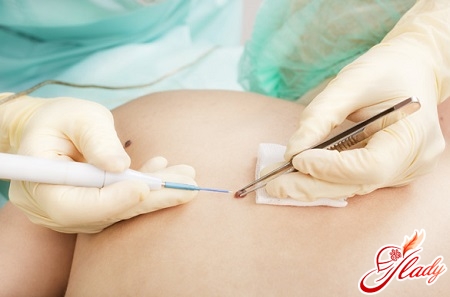
The localization sites of molluscum in a child may beare quite diverse: it can be the skin of the hands, neck, face, inner thighs and even the genitals. Feet and palms are never affected by the molluscum contagiosum virus. Since the molluscum contagiosum virus has no special manifestations, except for neoplasms in the form of nodules, it is confused with warts or with manifestations of measles and rubella. These diseases can be very easily distinguished by pressing on the neoplasm with tweezers: when the skin is infected with molluscum contagiosum, a granular white mass will begin to flow out of its center. Usually, children attending preschool institutions are susceptible to this virus. The virus is transmitted through household (clothing, toys, hygiene products, swimming pools) or physical contact (epidemics of this disease are common in kindergartens). Timely detection of neoplasms on the child's body will prevent them from spreading to other areas of the skin. It is important to remember that the growths can multiply even after their removal, so periodic examinations of the child's skin are necessary. Children rarely recover on their own, therefore, the formation of giant nodules is quite possible, which is why you should consult a dermatologist so that he can prescribe treatment. Only after consultation and examination of the patient by a doctor, you can start any action. The growths should be removed (laser, liquid nitrogen, Volkmann spoon) using anesthetics. Then you can continue the treatment with antiviral drugs and a certain treatment of the areas of the skin where the nodules were previously located, to prevent their reappearance. Everything should be prescribed by a doctor. After all the growths have been removed, it is imperative to wash all the child's clothes, bedding, and also treat personal hygiene items and toys. Until recovery, it is necessary to limit the sick child's contacts with other children.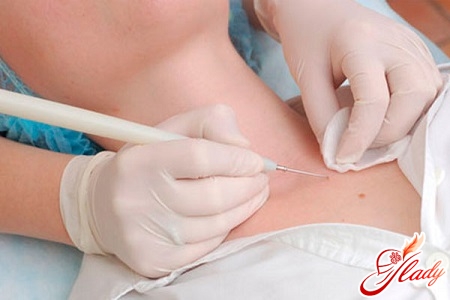
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in adults
When diagnosing the virus in an adultThe doctor may suggest that the patient wait until the body recovers on its own. This suggestion is made in the absence of malignant or benign formations. The patient's body with normal immunity can overcome the symptoms of this disease on its own in six months. In cases where the stage of the disease (severity of symptoms) and the state of the patient's immunity do not allow for spontaneous recovery, the following treatment methods are used:
- extrusion of the contents of the neoplasms, and then its scraping with Volkmann's spoon (after the procedure the skin is treated with iodine);
- treatment of neoplasms with antiviral ointments and immunomodulators;
- removal by current;
- cauterization with nitrogen;
- the appointment of a course of antibiotics (used for severe damage to the skin);
- laser removal of mollusks.
All treatment methods are selected individually by a doctor.
Prevention of molluscum contagiosum
The main preventive measures are based, of course,same, for timely diagnosis of the disease and its correct treatment, in this regard, it is necessary to conduct regular preventive examinations of the body. In preschool institutions, regular change of bed linen is mandatory, and parents should monitor the child's compliance with hygiene rules at home (changing linen, using a personal washcloth and towel, daily mandatory shower). For adults, the main preventive measure is confidence in the health of the sexual partner. In case of infection, you must refuse sexual contact.