 If your pregnancy is normal, then28 weeks you are recommended to visit the gynecologist monthly, after 28 weeks - twice as often. Prepare yourself that during each visit you will need to pass a general analysis of blood and urine. At least two ultrasound examinations are waiting for you, but it is better to do five screenings: at 6–8 (for early registration), for 12, 22, 32, and 36–38 weeks. What else? Let's run through the weeks of pregnancy and make a schedule of tests and diagnostic procedures.
If your pregnancy is normal, then28 weeks you are recommended to visit the gynecologist monthly, after 28 weeks - twice as often. Prepare yourself that during each visit you will need to pass a general analysis of blood and urine. At least two ultrasound examinations are waiting for you, but it is better to do five screenings: at 6–8 (for early registration), for 12, 22, 32, and 36–38 weeks. What else? Let's run through the weeks of pregnancy and make a schedule of tests and diagnostic procedures. A photo: GettyImages The test showed two bars Most likely, you have the first week of delay. This is about 5-6 obstetric weeks of pregnancy. Obstetric weeks are counted from the first day of the last menstruation, that is, in fact, even before ovulation, in which conception took place. Why is that? Ovulation in women occurs on different days of the cycle, and in some cycles there may even be two ovulations. It is not known exactly on which particular day the conception took place and, moreover, when the embryo penetrated the uterine mucosa. Therefore, obstetricians are counting the gestation period from the day of the beginning of the maturation of the egg, that is, from the first day of the last menstruation. 5–6 weeks. You can already be registered in the antenatal clinic. Early registration at least will provide an opportunity to determine whether the pregnancy is uterine. Unfortunately, even the most expensive pharmacy pregnancy test responds only to the presence of hCG in the urine, but does not determine its quantity, which is important for the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. At the reception, the gynecologist will definitely prescribe a laboratory blood test for HCG - determining the amount of the hormone will help exclude or confirm an ectopic pregnancy and establish the time limit as accurately as possible. 7–8 weeks. Waiting for an ultrasound scan on which you can already see the embryo and hear its heartbeat. You will visit the doctor again. He will conduct an examination, check the chest, prescribe the necessary tests and consultations of other specialists to get a complete picture of your health. It is important to pass a general analysis of blood, urine, smear for flora, determine blood type and Rh factor (Rh factor), sugar level, make a coagulogram (check blood clotting), HIV test, hepatitis, RW and TORCH infection. negative rhesus in the mother and his combination with positive rhesus the father has the likelihood of rhesus conflict, but only if the fetus “takes” the positive rhesus of the father. Therefore, when a negative Rh factor is detected in a woman, the spouse must be examined. If the Rhesus-conflict nevertheless has arisen, then it will be necessary to donate blood every month before the 32nd week of pregnancy each month to determine the level of antibodies, then - more often. In order to neutralize possible anti-rhesus antibodies, an antiglobulin D is administered to the expectant mother on the 30th week. The indicators of the coagulogram are also very important. This is a study of the blood clotting system. Since during the pregnancy the mother’s body produces the so-called third circle of the blood circulation - the uterine-placental - it is very important to monitor the blood clotting parameters. Disorders in the hemostatic system threaten complications that are extremely dangerous for pregnancy. TORCH infections are a group of especially dangerous infections that can be transmitted from mother to fetus, causing serious and irreversible developmental disorders. There are four of them: toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus and herpes. It is best even during the planning of pregnancy to pass a blood test for the determination of antibodies to these diseases and take root for infections.
A photo: GettyImages The test showed two bars Most likely, you have the first week of delay. This is about 5-6 obstetric weeks of pregnancy. Obstetric weeks are counted from the first day of the last menstruation, that is, in fact, even before ovulation, in which conception took place. Why is that? Ovulation in women occurs on different days of the cycle, and in some cycles there may even be two ovulations. It is not known exactly on which particular day the conception took place and, moreover, when the embryo penetrated the uterine mucosa. Therefore, obstetricians are counting the gestation period from the day of the beginning of the maturation of the egg, that is, from the first day of the last menstruation. 5–6 weeks. You can already be registered in the antenatal clinic. Early registration at least will provide an opportunity to determine whether the pregnancy is uterine. Unfortunately, even the most expensive pharmacy pregnancy test responds only to the presence of hCG in the urine, but does not determine its quantity, which is important for the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. At the reception, the gynecologist will definitely prescribe a laboratory blood test for HCG - determining the amount of the hormone will help exclude or confirm an ectopic pregnancy and establish the time limit as accurately as possible. 7–8 weeks. Waiting for an ultrasound scan on which you can already see the embryo and hear its heartbeat. You will visit the doctor again. He will conduct an examination, check the chest, prescribe the necessary tests and consultations of other specialists to get a complete picture of your health. It is important to pass a general analysis of blood, urine, smear for flora, determine blood type and Rh factor (Rh factor), sugar level, make a coagulogram (check blood clotting), HIV test, hepatitis, RW and TORCH infection. negative rhesus in the mother and his combination with positive rhesus the father has the likelihood of rhesus conflict, but only if the fetus “takes” the positive rhesus of the father. Therefore, when a negative Rh factor is detected in a woman, the spouse must be examined. If the Rhesus-conflict nevertheless has arisen, then it will be necessary to donate blood every month before the 32nd week of pregnancy each month to determine the level of antibodies, then - more often. In order to neutralize possible anti-rhesus antibodies, an antiglobulin D is administered to the expectant mother on the 30th week. The indicators of the coagulogram are also very important. This is a study of the blood clotting system. Since during the pregnancy the mother’s body produces the so-called third circle of the blood circulation - the uterine-placental - it is very important to monitor the blood clotting parameters. Disorders in the hemostatic system threaten complications that are extremely dangerous for pregnancy. TORCH infections are a group of especially dangerous infections that can be transmitted from mother to fetus, causing serious and irreversible developmental disorders. There are four of them: toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus and herpes. It is best even during the planning of pregnancy to pass a blood test for the determination of antibodies to these diseases and take root for infections.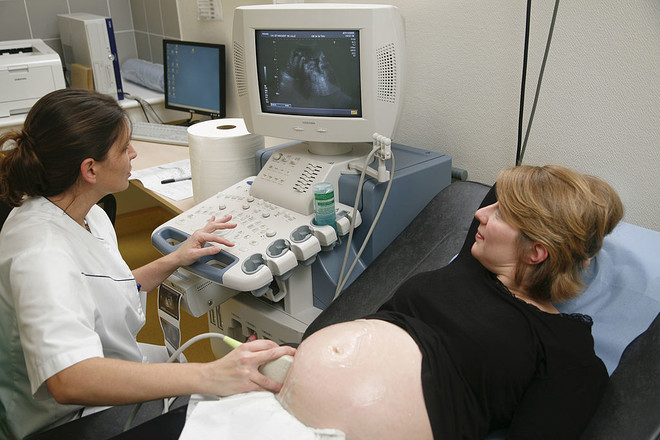 Photo:GettyImages10 weeksYou will visit your doctor again to determine the tactics for managing your pregnancy based on the results of tests, diagnostic procedures and opinions of specialists in other fields.11-13 weeksYou will have prenatal screening, which identifies fetal malformations already in the early stages of pregnancy. Screening consists of an ultrasound and a blood test. During the ultrasound, the parameters and sizes of certain areas of the fetus's body are measured, and then the results are compared with the standard indicators. Blood is donated for the PAPP-A test and to determine the level of hCG. This is the so-called "double test". The PAPP-A test detects the level of a special protein that is produced by the placenta and should steadily increase as the fetus develops.12-14 weeksDuring this period, you will need to consult with your doctor based on the screening results and decide on the advisability of visiting a geneticist.16 weeksWe take another urine and blood test, but this time the blood is needed for two things: - determining the level of hemoglobin and excluding the development of anemia, which is dangerous for the health of the child; – determination of the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This diagnostic test also provides clarity regarding the presence or absence of chromosomal pathology in the fetus. 16-18 weeksHere, the cervix is carefully examined to exclude ICI (isthmic-cervical insufficiency), that is, its shortening. Cervicometry is performed - measuring the length of the cervix using ultrasound. Or an examination on the chair.20-21 weeksAnother screening ultrasound and a scheduled examination by a doctor are performed.24 weeksWe undergo a glucose tolerance test to detect gestational diabetes.28 weeksA scheduled visit to the gynecologist, a control blood test to detect Rh antibodies.30 weeksLabor is coming soon! Therefore, you will receive a birth certificate and an exchange card. During this period, the choice of the method of delivery begins. For this, it is important to determine the position of the fetus, so an ultrasound and examination are mandatory!
Photo:GettyImages10 weeksYou will visit your doctor again to determine the tactics for managing your pregnancy based on the results of tests, diagnostic procedures and opinions of specialists in other fields.11-13 weeksYou will have prenatal screening, which identifies fetal malformations already in the early stages of pregnancy. Screening consists of an ultrasound and a blood test. During the ultrasound, the parameters and sizes of certain areas of the fetus's body are measured, and then the results are compared with the standard indicators. Blood is donated for the PAPP-A test and to determine the level of hCG. This is the so-called "double test". The PAPP-A test detects the level of a special protein that is produced by the placenta and should steadily increase as the fetus develops.12-14 weeksDuring this period, you will need to consult with your doctor based on the screening results and decide on the advisability of visiting a geneticist.16 weeksWe take another urine and blood test, but this time the blood is needed for two things: - determining the level of hemoglobin and excluding the development of anemia, which is dangerous for the health of the child; – determination of the level of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This diagnostic test also provides clarity regarding the presence or absence of chromosomal pathology in the fetus. 16-18 weeksHere, the cervix is carefully examined to exclude ICI (isthmic-cervical insufficiency), that is, its shortening. Cervicometry is performed - measuring the length of the cervix using ultrasound. Or an examination on the chair.20-21 weeksAnother screening ultrasound and a scheduled examination by a doctor are performed.24 weeksWe undergo a glucose tolerance test to detect gestational diabetes.28 weeksA scheduled visit to the gynecologist, a control blood test to detect Rh antibodies.30 weeksLabor is coming soon! Therefore, you will receive a birth certificate and an exchange card. During this period, the choice of the method of delivery begins. For this, it is important to determine the position of the fetus, so an ultrasound and examination are mandatory! Photo:GettyImages32 weeksA follow-up examination by a doctor with measurement of all parameters and ultrasound.30-34 weeksA CTG of the fetus is performed for the first time, based on the results of which the capabilities of the cardiovascular system of the fetus are assessed and a conclusion is made about the presence or absence of intrauterine hypoxia.34-40 weeksA doctor's examination with constant monitoring of the protein level in the urine. An increase in protein levels may be a sign of the development of late toxicosis - gestosis. During the same period, an ultrasound is performed again to monitor the position of the fetus, determine the condition of the umbilical cord, placenta and clarify the method of delivery. Essence
Photo:GettyImages32 weeksA follow-up examination by a doctor with measurement of all parameters and ultrasound.30-34 weeksA CTG of the fetus is performed for the first time, based on the results of which the capabilities of the cardiovascular system of the fetus are assessed and a conclusion is made about the presence or absence of intrauterine hypoxia.34-40 weeksA doctor's examination with constant monitoring of the protein level in the urine. An increase in protein levels may be a sign of the development of late toxicosis - gestosis. During the same period, an ultrasound is performed again to monitor the position of the fetus, determine the condition of the umbilical cord, placenta and clarify the method of delivery. Essence

Making Money with Desserts: Success Stories
Evgeniya Polischuk (Fedutinova) instagram:@evgeniyafedutinovavk.com/janeshomebaking– It all started with baking for family and friends. Gradually, I started posting photos of my baked goods on Instagram – and orders started coming in. I made my first custom-made cake on October 13, 2014, and a little earlier I started making macaroons and cupcakes. You could say that the business “found me”, I am very […]

Soups are cold recipes with photos
Cold cucumber soup with yogurt and lemonsorbet from the chef of the restaurant La Taverna Alexander Zhurkin Photo: Getty Images Ingredients: Plain yoghurt – 125 g Cucumber – 150 g Lemon/lime sorbet – 50 g Cocktail shrimp – 24 g Fresh ginger juice – 1 g Lime juice – 5 g Fresh orange juice – 5 g Parsley – 1 g Pink pepper – 1 g Watercress – […]

barbeque kebab
Pork tenderloin in glaze Photo:Dmitry Bayrak/dbstudioPreparation time: 20 minutes + marinating time.Calories: 454 kcal per serving.For 4 servings: 4 pork tenderloins (approximately 300 g each), 1 onion, 2 cloves of garlic, 1 tsp. lemon zest, 1 tsp. lemon juice, a pinch of ground cumin, coriander and turmeric, 1 tbsp. vegetable […]

Pierre Duacan: dietary recipes: Ducane diet
Beetroot soup Photo:Season’S, Luxury Hotels RepresentationYou will need:· Boiled beetroot – 60 g· Fresh cucumbers – 20 g· Red radish – 20 g· Green onions – 10 g· Egg – 1 pc.· Drinking mineral water – 200 g· Salt – 1 gPreparation:· Boil the egg and beetroot.· Grate the cucumbers, radish and part of the beetroot. Put everything […]





