Symptoms of external otitis media
The disease is caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria,staphylococci, mold fungi or yeast. The hostile flora affects the cartilage, earlobe and skin of the auricle to the eardrum. Infants begin to cry loudly and shake their heads, tilting them toward the sore ear. Older children complain of itching and severe pain.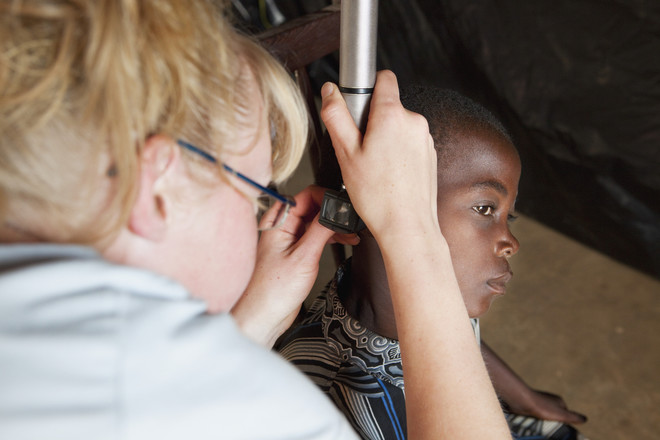 Otitis externa in children is a serious diseasePhoto: Getty Parents should immediately examine the child's ears. Usually, the disease makes itself known by the following signs:
Otitis externa in children is a serious diseasePhoto: Getty Parents should immediately examine the child's ears. Usually, the disease makes itself known by the following signs:
- redness and swelling of the auricle;
- severe pain when pressing on a tragus;
- small bubbles with liquid contents;
- furuncles;
- discharge with putrefactive odor.
Children may complain of a feeling of congestion,hearing loss, dizziness. The temperature rises to + 38 - 39° C. The next step for parents is an immediate visit to the doctor. The disease has various forms - from earwax to diffuse inflammation and erysipelas. Therefore, it is impossible to use folk remedies and independently select medications.
How do doctors treat otitis externa in a child?
After examination and tests by a pediatric otolaryngologistprescribe medications. Antimicrobial, antipyretic and analgesic drugs are prescribed for erysipelas, perichondritis and general inflammation. Mature boils require surgical opening, and earwax requires ear lavage. Antifungal tablets and ointments are necessary for fungal and yeast infections. External remedies play an important role - ear drops, turundas with alcohol, iodine, hydrogen peroxide, as well as UHF and UV therapy. The doctor will recommend that parents organize a vitamin-rich diet for the child. Since it is difficult to swallow with ear pain, the food should be soft - soups, porridge, jelly, vegetable and fruit purees. The baby needs rest. Visits from other children are not allowed - many forms of otitis are contagious. The ears should be cleaned twice a day with a disinfectant solution. External otitis is a serious threat. Spreading rapidly to the inner ear, the infection can lead to purulent inflammation, hearing loss and meningitis. To prevent the disease from recurring in the future, it is necessary to carefully observe ear hygiene and strengthen the child's immunity. Read also: